推薦產品
描述
0.2 μm sterile filtered
suitable for 3D bioprinting applications
品質等級
形狀
gel form (viscous)
雜質
≤5 CFU/g Bioburden (Fungal)
≤5 CFU/g Bioburden (Total Aerobic)
顏色
white
pH值
6.5-7.5
應用
3D bioprinting
儲存溫度
2-8°C
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
應用
TissueFab®- GelMA-Bone-UV bioink is designed for promoting osteogenic differentiation of stem cells. It is based on Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) - Hydroxyapatite (HAp) hydrogel system. HAp is a highly crystalline form of calcium phosphate. HAp has a chemical similarity with the mineralized phase of bone which accounts for their excellent biocompatibility and osteoinductive and osteoconductive properties favorable for bone regeneration. HAp-containing hydrogels has been studied in literature to demonstrate their processability with different additive manufacturing approaches. Printing of cell laden structures with HAp containing bioink formulations have shown superior osteogenic properties.
法律資訊
TISSUEFAB is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Tunable hydrogel composite with two-step processing in combination with innovative hardware upgrade for cell-based threedimensional bioprinting
Wust S, et al.
Acta Biomaterialia, 10, 630?40-630?40 (2014)
Tunable hydrogel composite with two-step processing in combination with innovative hardware upgrade for cell-based threedimensional bioprinting.
Wust S. et al.
Acta Biomaterialia, 10, 630-640 (2014)
Nano hydroxyapatite particles promote osteogenesis in a three-dimensional bio-printing construct consisting of alginate/gelatin/hASCs
Wang X F et al.
Royal Society of Chemistry Advances, 6, 6832-6842 (2016)
Mehdi Sadat-Shojai et al.
Materials science & engineering. C, Materials for biological applications, 49, 835-843 (2015-02-18)
The ability to encapsulate cells in three-dimensional (3D) protein-based hydrogels is potentially of benefit for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. However, as a result of their poor mechanical strength, protein-based hydrogels have traditionally been considered for soft tissue engineering only.
Yicong Zuo et al.
ACS applied materials & interfaces, 7(19), 10386-10394 (2015-05-01)
Modular tissue engineering holds great potential in regenerating natural complex tissues by engineering three-dimensional modular scaffolds with predefined geometry and biological characters. In modular tissue-like construction, a scaffold with an appropriate mechanical rigidity for assembling fabrication and high biocompatibility for
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務




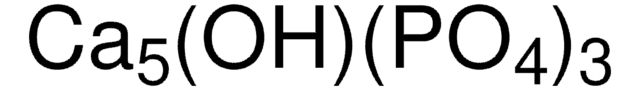
![聚[(R)-3-羟基丁酸] natural origin](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/129/476/7d1c924b-f644-4889-a2d6-d7a923ce382c/640/7d1c924b-f644-4889-a2d6-d7a923ce382c.png)

