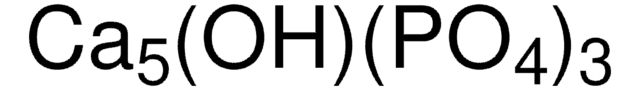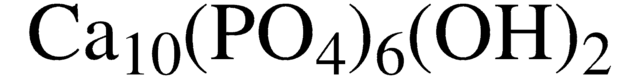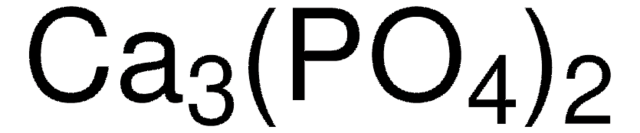推薦產品
等級
for analytical purposes
化驗
≥97%
形狀
nanopowder
solid
表面積
>9.4 m2/g
粒徑
<200 nm (BET)
mp
1100 °C (lit.)
SMILES 字串
[Ca++].[Ca++].[Ca++].[Ca++].O[Ca+].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O
InChI
1S/5Ca.3H3O4P.H2O/c;;;;;3*1-5(2,3)4;/h;;;;;3*(H3,1,2,3,4);1H2/q5*+2;;;;/p-10
InChI 密鑰
XYJRXVWERLGGKC-UHFFFAOYSA-D
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
一般說明
應用
聚(4-苯乙烯磺酸钠)修饰的羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒可作为万古霉素的药物载体。羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒可控制支架植入体内后抗生素的释放。
多孔羟基磷灰石微球对重金属具有较高的吸附能力,可用于重金属污染水体的处理。
特點和優勢
- 生物活性和生物相容性
- 机械强度好
- 多孔结构
- 骨传导和骨整合特性
法律資訊
儲存類別代碼
13 - Non Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
客戶也查看了
文章
Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications
Innovation in dental restorative materials is driven by the need for biocompatible and natural-appearing restoration alternatives. Conventional dental materials like amalgam and composite resins have inherent disadvantages.
A key challenge for nanomaterial safety assessment is the ability to handle the large number of newly engineered nanomaterials (ENMs), including developing cost-effective methods that can be used for hazard screening.
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務