SML2784
CMPD101 hydrochloride
≥98% (HPLC)
别名:
3-((4-Methyl-5-(pyridin-4-yl)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methylamino)-N-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl)benzamide, 3-[[[4-Methyl-5-(4-pyridinyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl]methyl]amino]-N-[[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methyl]benzamide hydrochloride, Compound 101 hydrochloride, Cpd101 hydrochloride, Takeda101 hydrochloride
登录查看公司和协议定价
所有图片(1)
About This Item
推荐产品
品質等級
化驗
≥98% (HPLC)
形狀
powder
儲存條件
desiccated
顏色
white to beige
溶解度
DMSO: 2 mg/mL, clear
儲存溫度
2-8°C
SMILES 字串
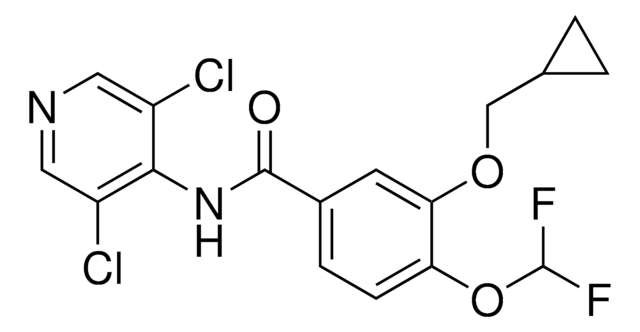
CN1C(CNC2=CC=CC(C(NCC3=CC=CC=C3C(F)(F)F)=O)=C2)=NN=C1C4=CC=NC=C4.Cl
生化/生理作用
CMPD101 is an active site-targeting, potent and subtype-selective G protein-coupled receptor kinase GRK2 & GRK3 inhibitor (human GRK2/3 IC50 = 54/32 nM with 3 μM ATP and tubulin dimer as substrate; bovine GRK2 IC50 = 290 nM with 0.5 mM ATP and bROS as substrate; no GRK1/5 inhibition at 125 μM). CMPD101 selectively inhibits GPR39 agonist-induced β-arrestin recruitment (by 94% at 10 μM against 30 μM GPR39-C3/50 μM ZnCl2), but not cAMP pathway desensitization in cultures and prevents β-arrestin2-biased D2R ligand UNC9994(1 μg/side bilateral local injection) from blocking NMDAR antagonist PCP (6 mg/kg i.p.)-induced locomotion (60%/12% blockage without/with 0.5 μg CMPD101 co-injection) in mice in vivo.
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Yuji Shimizu et al.
Biochemical pharmacology, 140, 105-114 (2017-06-18)
GPR39, a G-protein-coupled receptor activated by zinc, reportedly activates multiple intracellular signaling pathways via Gs, Gq, G12/13, and β-arrestin, but little is known about downregulation of the receptor upon its activation. To our knowledge, this is the first report on
Jesse J DiCello et al.
American journal of physiology. Gastrointestinal and liver physiology, 317(2), G79-G89 (2019-05-16)
Endocytosis is a major mechanism through which cellular signaling by G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) is terminated. However, recent studies demonstrate that GPCRs are internalized in an active state and continue to signal from within endosomes, resulting in effects on cellular
Alessandro Cannavo et al.
Frontiers in pharmacology, 10, 888-888 (2019-08-27)
Hyperaldosteronism alters cardiac function, inducing adverse left ventricle (LV) remodeling either via increased fibrosis deposition, mitochondrial dysfunction, or both. These harmful effects are due, at least in part, to the activation of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2). In
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门
![1,2,3,4-四氢-9H-吡啶并[3,4-b]吲哚 98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/181/460/3d58bc34-1b5c-4295-bbac-3b52085670e8/640/3d58bc34-1b5c-4295-bbac-3b52085670e8.png)