推荐产品
化驗
≥98% (HPLC)
形狀
powder
顏色
white to beige
溶解度
DMSO: 2 mg/mL, clear
儲存溫度
2-8°C
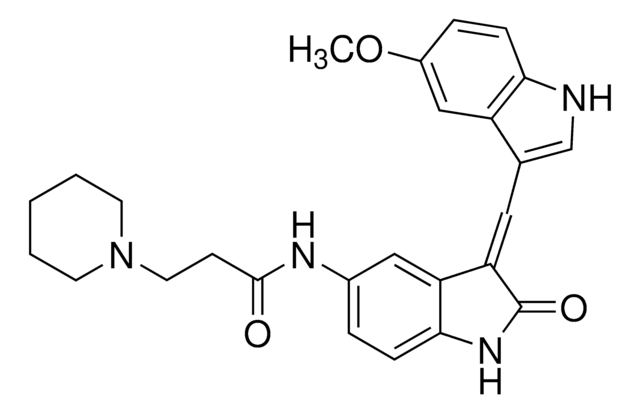
SMILES 字串
O=C1C=C(C2=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C2)NC3=C(C4=CC=C(Cl)C=C4)C(CC5=CC=CC=C5)=NN31
InChI
1S/C25H17ClN4O3/c26-19-10-6-18(7-11-19)24-22(14-16-4-2-1-3-5-16)28-29-23(31)15-21(27-25(24)29)17-8-12-20(13-9-17)30(32)33/h1-13,15,27H,14H2
InChI 密鑰
GUUWHOSUKOCRHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
生化/生理作用
Inhibitor against ArfGEF ARNO- and BRAG2/GEP100-dependent ARF1/6 activity. Inhibits melanoma growth in vitro and in vivo.
NAV-2729 (IC50 of 1.5 μM) has a therapeutic benefit in reducing the adverse effect of diabetic retinopathy in animal models.
Originally characterized as a non-nucleotide-competitive and reversible ARF6-selective inhibitor (IC50 = 1.4 μM without GEF and 2.4 μM with 100 nM ARNO or BRAG2/GEP100) that targets ARF6 GEF-binding region, NAV-2729 prevents GEF-dependent ARF1 & ARF6 activity (% inhibition of BRAG2Sec7PH-stimulated GTPase activity/[NAV-2729] = 50% Δ17Arf1/10 μM and 15% Δ13Arf6/25 μM) with higher potency against BRAG2- than ARNO-dependent ARF1 activity (64% vs. 20% Δ17Arf1 inhibition at 25 μM in the presence of respective GEF sec7 domain). NAV-2729 treatment effectively inhibits G-alpha-q downstream signaling pathways and anchorage-independent colony growth of Mel92.1 & Mel202 melanoma cells in vitro (10 μM) as well as uveal melanoma tumor establishment in Mel202 xenograft mice in vivo (30 mg/kg/day i.p.).
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Yohei Yamauchi et al.
Advances in biological regulation, 63, 115-121 (2016-10-26)
The Small GTPase ADP-ribosylation factor 6 (Arf6) functions as the molecular switch in cellular signaling pathways by cycling between GDP-bound inactive and GTP-bound active form, which is precisely regulated by two regulators, guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) and GTPase-activating proteins
Jae Hyuk Yoo et al.
Cancer cell, 29(6), 889-904 (2016-06-07)
Activating mutations in Gαq proteins, which form the α subunit of certain heterotrimeric G proteins, drive uveal melanoma oncogenesis by triggering multiple downstream signaling pathways, including PLC/PKC, Rho/Rac, and YAP. Here we show that the small GTPase ARF6 acts as
Weiquan Zhu et al.
The Journal of clinical investigation, 127(12), 4569-4582 (2017-10-24)
The devastating sequelae of diabetes mellitus include microvascular permeability, which results in retinopathy. Despite clinical and scientific advances, there remains a need for new approaches to treat retinopathy. Here, we have presented a possible treatment strategy, whereby targeting the small
Sarah Benabdi et al.
Biochemistry, 56(38), 5125-5133 (2017-09-01)
Arf GTPases and their guanine nucleotide exchange factors (ArfGEFs) are major regulators of membrane traffic and organelle structure in cells. They are associated with a variety of diseases and are thus attractive therapeutic targets for inhibition by small molecules. Several
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门