推荐产品
品質等級
化驗
≥98% (HPLC)
形狀
powder
顏色
white to beige
溶解度
DMSO: ≥10 mg/mL, clear
儲存溫度
−20°C
SMILES 字串
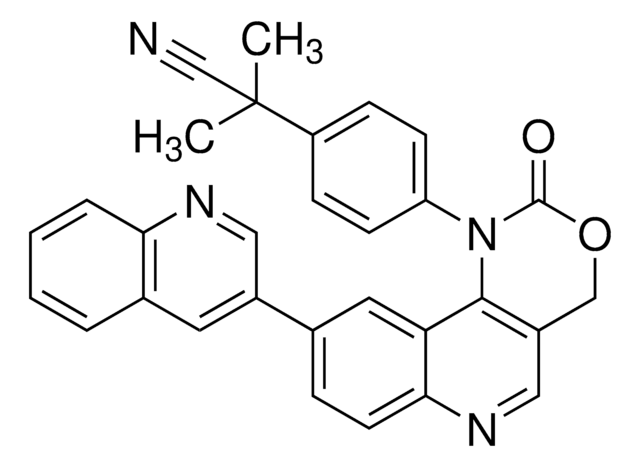
CS(C(C=C1)=CC=C1C2=NC(C(NC3=CC=CC=C3)=O)=C(N)N=C2)(=O)=O
InChI
1S/C18H16N4O3S/c1-26(24,25)14-9-7-12(8-10-14)15-11-20-17(19)16(22-15)18(23)21-13-5-3-2-4-6-13/h2-11H,1H3,(H2,19,20)(H,21,23)
InChI 密鑰
DUIHHZKTCSNTGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
應用
VE-821 已用作人癌细胞中 ATM 和 Rad3 相关(ATR)蛋白的抑制剂。
生化/生理作用
VE-821 是一种有效的 ATP 竞争性抑制剂,可抑制 DNA 损伤应答(DDR)激酶共济失调毛细血管扩张突变(ATM)以及与 ATM 和 Rad3 相关(ATR),Ki 值为 13 nM。VE-821 对相关 PIKKs ATM、DNA 依赖性蛋白激酶(DNA-PK)、mTOR 和 PI3-激酶-γ 的交叉反应极小(Ki 值分别为 16 μM、2.2 μM、>1 μM 和 3.9 μM),并针对大量无关的蛋白激酶。在大部分癌细胞中单独使用 VE-821 会导致细胞死亡,并且还显示出与遗传毒性剂的强大协同作用。VE-821 增加了细胞对放射线的敏感性,并使癌细胞对多种化学治疗剂敏感。
其他說明
VE-821 已由化学探针门户网站进行了专家审查和推荐。有关更多信息,请访问化学探针门户网站上的 VE-821 探针摘要。
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
其他客户在看
Anastazja Poczta et al.
Scientific reports, 9(1), 14135-14135 (2019-10-03)
The present study investigated the effect of cladribine (CLA) and six of its derivatives containing a formamidine group at position 6 (CLA-FDM, CLA-FPAZ, CLA-FPIR, CLA-FPIP, CLA-FHEX, and CLA-FMOR) on acute promyelocytic, lymphoblastic, and acute monocytic leukemia cells. The role of
Human cancer cells utilize mitotic DNA synthesis to resist replication stress at telomeres regardless of their telomere maintenance mechanism
Ozgun Ozer, et al.
Oncotarget null
Tingting Li et al.
Aging, 12(14), 14791-14807 (2020-07-21)
Protection of telomere 1 (POT1), the telomeric single-stranded DNA (ssDNA)-binding protein in the shelterin complex, has been implicated in the DNA damage response, tumorigenesis and aging. Telomere dysfunction induced by telomere deprotection could accelerate cellular senescence in primary human cells.
Aaron Mendez-Bermudez et al.
Molecular cell, 70(3), 449-461 (2018-05-05)
Hard-to-replicate regions of chromosomes (e.g., pericentromeres, centromeres, and telomeres) impede replication fork progression, eventually leading, in the event of replication stress, to chromosome fragility, aging, and cancer. Our knowledge of the mechanisms controlling the stability of these regions is essentially
Camelia Mocanu et al.
Cell reports, 39(3), 110701-110701 (2022-04-21)
Mitotic DNA synthesis (MiDAS) has been proposed to restart DNA synthesis during mitosis because of replication fork stalling in late interphase caused by mild replication stress (RS). Contrary to this proposal, we find that cells exposed to mild RS in
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门