推荐产品
生物源
rabbit
品質等級
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
affinity isolated antibody
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
分子量
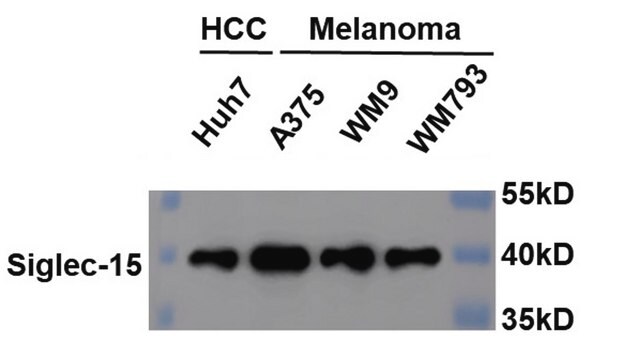
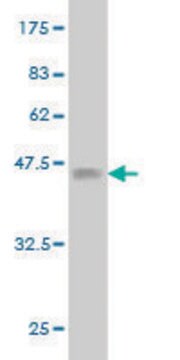
36 kDa
物種活性
human, rat, mouse
濃度
1 mg/mL
技術
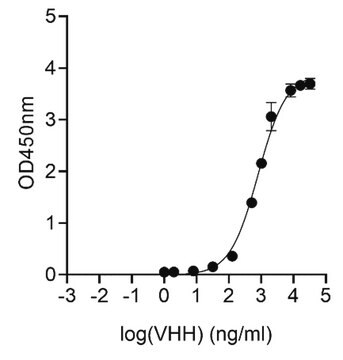
ELISA: suitable
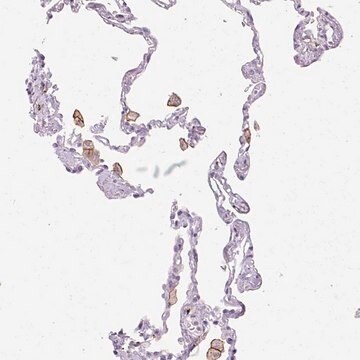
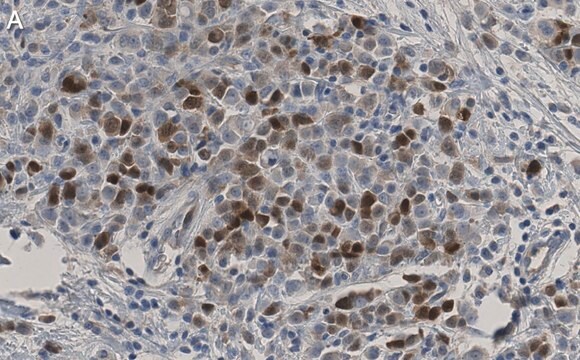
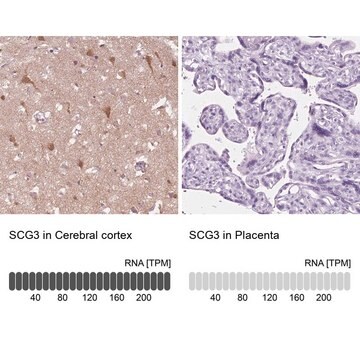
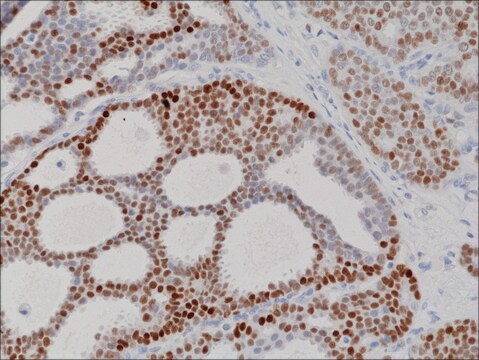
immunohistochemistry: suitable
western blot: suitable
NCBI登錄號
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
wet ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... SIGLEC15(284266)
一般說明
唾液酸结合性免疫球蛋白样凝集素15(SIGLEC15)是聚糖识别蛋白Siglec家族的一部分。它在巨噬细胞的子类中表达。这种I型跨膜蛋白具有两个免疫球蛋白样结构域,一个跨膜结构域和一个短的胞质尾巴。SIGLEC15基因位于人类染色体18q12.3上。
免疫原
该抗体通过靶向人SIGLEC15的氨基末端附近的15个氨基酸多肽获得。
生化/生理作用
唾液酸结合性免疫球蛋白样凝集素15(SIGLEC15)可以识别称为唾液酸-Tn(sTn)抗原的肿瘤相关聚糖结构。它在肿瘤组织中与肿瘤相关的巨噬细胞中表达。该蛋白质可充当信号转导子。SIGLEC15可与12kDa的衔接子蛋白DNAX激活蛋白(DAP12)结合,并将信号转导至脾酪氨酸激酶(Syk)。
特點和優勢
完放心地使用我们的抗体。如果抗体在您的申请的研究中不起作用,我们将全额退款或安排替代抗体。了解更多信息。
聯結
可以使用阻断肽 SBP3500654阻断该抗体的作用。
外觀
以1 mg/mL浓度,溶于含0.02%叠氮化钠的PBS溶液的形式提供。
免責聲明
除非我们的产品目录或产品附带的其他公司文档另有说明,否则我们的产品仅供研究使用,不得用于任何其他目的,包括但不限于未经授权的商业用途、体外诊断用途、离体或体内治疗用途或任何类型的消费或应用于人类或动物。
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Siglec-15: an immune system Siglec conserved throughout vertebrate evolution.
Glycobiology (2007)
The interaction between Siglec-15 and tumor-associated sialyl-Tn antigen enhances TGF-? secretion from monocytes/macrophages through the DAP12-Syk pathway.
Takamiya R
Glycobiology (2013)
Jiao Hu et al.
Theranostics, 11(7), 3089-3108 (2021-02-05)
Rationale: Siglec15 is an emerging target for normalization cancer immunotherapy. However, pan-cancer anti-Siglec15 treatment is not yet validated and the potential role of Siglec15 in bladder cancer (BLCA) remains elusive. Methods: We comprehensively evaluated the expression pattern and immunological role
Kaiqin Sheng et al.
International journal of molecular sciences, 24(1) (2023-01-09)
Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin 15 (Siglec-15) has been identified as a crucial immune suppressor in human cancers, comparable to programmed cell death 1 ligand (PD-L1). However, the regulatory mechanisms underlying its transcriptional upregulation in human cancers remain largely unknown. Here
Comparative genomics indicates the mammalian CD33rSiglec locus evolved by an ancient large-scale inverse duplication and suggests all Siglecs share a common ancestral region
Huan Cao
Immunogenetics, 401-477 (2009)
Global Trade Item Number
| 货号 | GTIN |
|---|---|
| SAB3500654-100UG | 4061832496412 |
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系客户支持