推荐产品
一般說明
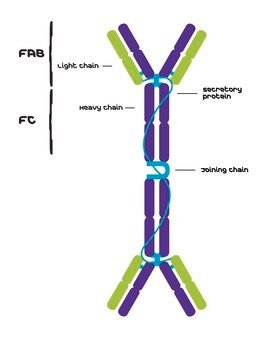
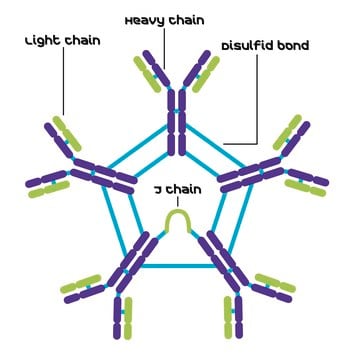
IgA 抗体是一种分泌型抗体,大量存在于胃肠道、呼吸道和泌尿生殖道粘膜、泪液和唾液中。因此分泌型 IgA 对黏膜表面病原体的体液防御机制起作用
IgA,κ来自小鼠骨髓瘤是由 TEPC 15 肿瘤系产生的,即在 BALB/c 小鼠中由姥鲛烷诱导的浆细胞瘤(起源于并经腹腔携带)。该抗体对 κ小鼠 IgA 链。纯化的免疫球蛋白制剂与抗小鼠 IgM、IgG1、IgG2a、IgG2b 和 IgG3 不反应。
IgA,κ来自小鼠骨髓瘤是由 TEPC 15 肿瘤系产生的,即在 BALB/c 小鼠中由姥鲛烷诱导的浆细胞瘤(起源于并经腹腔携带)。该抗体对 κ小鼠 IgA 链。纯化的免疫球蛋白制剂与抗小鼠 IgM、IgG1、IgG2a、IgG2b 和 IgG3 不反应。
产生小鼠IgA,k的TEPC 15肿瘤系是姥鲛烷诱导的浆细胞瘤,来源于BALB / c小鼠并存在于腹膜内。免疫球蛋白G(IgG)属于免疫球蛋白家族,是一种广泛表达的血清抗体。免疫球蛋白是由两条重链和两条轻链通过二硫键连接而成的。它主要用于帮助免疫防御。IgG是一种主要的免疫球蛋白。小鼠具有五种类型的免疫球蛋白 - IgM,IgG,IgA,IgD和IgE。血清中的IgA分子大部分为二聚体。IgA存在于唾液、气管支气管分泌物、泌尿生殖道分泌物、乳和初乳中。
特異性
抗原特异性:磷酸胆碱
應用
抗小鼠 IgA,κ在 ELISA 和免疫荧光中使用抗体作为二抗。
来自鼠类骨髓瘤的IgA,κ抗体已被用于:
- 免疫荧光测定
- 酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA)
- 侵袭试验
- 免疫印迹
生化/生理作用
免疫球蛋白G (IgG) 有助于调理素作用、补体结合和抗体依赖型细胞介导的细胞毒性作用。
外觀
0.02 MTris 缓冲盐溶液,pH 8.0,含 0.02% 叠氮化钠
免責聲明
除非我们的产品目录或产品附带的其他公司文档另有说明,否则我们的产品仅供研究使用,不得用于任何其他目的,包括但不限于未经授权的商业用途、体外诊断用途、离体或体内治疗用途或任何类型的消费或应用于人类或动物。
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
其他客户在看
AdcAII of Streptococcus pneumoniae affects pneumococcal invasiveness
Brown LR, et al.
PLoS ONE, 11(1), e0146785-e0146785 (2016)
Julio Villena et al.
The Journal of nutrition, 135(6), 1462-1469 (2005-06-03)
We studied the effect of Lactobacillus casei CRL 431 used as a supplement in a repletion diet on the resistance to Streptococcus pneumoniae respiratory infection in malnourished mice. Weaned mice were malnourished after they consumed a protein-free diet (PFD) for
Lindsey R Brown et al.
Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology, 7, 233-233 (2017-06-24)
Bacteria growing within biofilms are protected from antibiotics and the immune system. Within these structures, horizontal transfer of genes encoding virulence factors, and promoting antibiotic resistance occurs, making biofilms an extremely important aspect of pneumococcal colonization and persistence. Identifying environmental
The Laboratory Rat (1998)
Carlos J Sanchez et al.
PloS one, 6(12), e28738-e28738 (2011-12-17)
It is unclear whether Streptococcus pneumoniae in biofilms are virulent and contribute to development of invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD). Using electron microscopy we confirmed the development of mature pneumococcal biofilms in a continuous-flow-through line model and determined that biofilm formation
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门