推荐产品
product name
Monoclonal Anti-Dystrophin antibody produced in mouse, clone MANDRA1, ascites fluid
生物源
mouse
品質等級
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
ascites fluid
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
MANDRA1, monoclonal
包含
15 mM sodium azide
物種活性
rat, human, mouse, fish
技術
indirect immunofluorescence: 1:100 using freshly dissected and frozen human or animal muscle tissue.
microarray: suitable
同型
IgG1
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... DMD(1756)
mouse ... Dmd(13405)
rat ... Dmd(24907)
一般說明
Dystrophin is a muscle membrane protein (427 kDa) which is absent, reduced or altered as a result of mutation in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies (DMD/BMD) or its homologue in the mouse. Severe DMD is associated with a marked dystrophin deficiency whereas patients with the milder form of DMD show less pronounced abnormalities of protein expression. Because abnormalities in the protein expression occur specifically in patients with these types of muscular dystrophy, dystrophin analysis may be used to distinguish these conditions from other neuromuscular diseases. Predictions from the sequence suggest a structural protein on the inner face of the membrane, consisting of a 25-repeat, rod-like triple-helical domain separating an N-terminal actin-binding domain from two C-terminal domains, one of which is rich in cysteine. The large size of dystrophin and its low abundance (<0.01% of the total muscle protein) are a hindrance to the isolation of intact, native protein for structure/function studies.
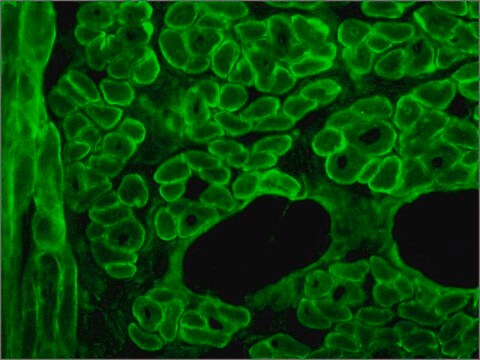
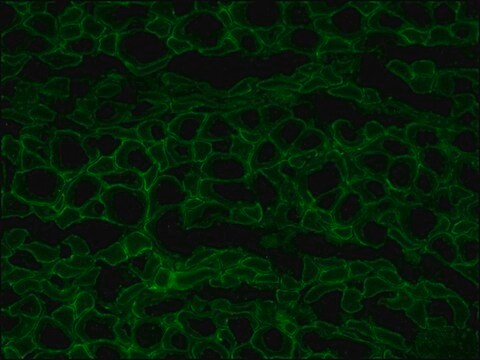
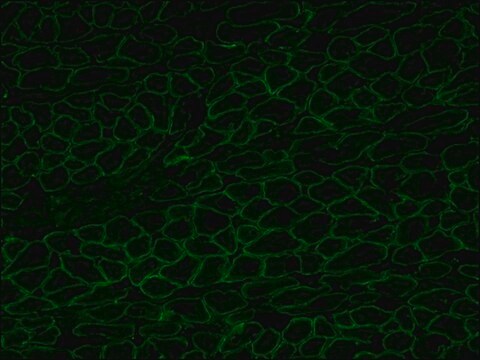
The antibody recognizes an epitope located on the 128 amino acids at the end of the C-terminal domain of the human dystrophin molecule (amino acid residues 3558-3684). Immunohistochemical staining of muscle tissue results in a clear labeling confined to the periphery (plasma membrane) of normal striated muscle fibers. By immunoblotting, the antibody stains dystrophin (427 kDa) in muscle and brain extracts. It also stains the 70-75 kDa protein known as Apo-Dystrophin-1 or Dp71.4 This is detected in the brain as well as in lymphoblastoid cells, cultures of brain astroglial and neuronal cells, liver and Hep G2 cells (human hepatoma). The epitope recognized by the antibody is sensitive to formalin fixation and paraffin embedding. The antibody exhibits a wide interspecies cross-reactivity. It is useful in ELISA and capture ELISA. The antibody is specific to dystrophin and does not react with α-actinin and utrophin, an autosomal homologue of dystrophin, also called dystrophin-related protein (DRP).
特異性
The antibody recognizes an epitope located on the 128 amino acids at the end of the C-terminal domain of the human dystrophin molecule (amino acid residues 3558-3684). Immunohistochemical staining of muscle tissue results in a clear labeling confined to the periphery (plasma membrane) of normal striated muscle fibers. By immunoblotting, the antibody stains dystrophin (427 kDa) in muscle and brain extracts. It also stains the 70-75 kDa protein known as Apo-Dystrophin-1 or Dp71.4 This is detected in the brain as well as in lymphoblastoid cells, cultures of brain astroglial and neuronal cells, liver and Hep G2 cells (human hepatoma). The epitope recognized by the antibody is sensitive to formalin fixation and paraffin embedding. The antibody exhibits a wide interspecies cross-reactivity. It is useful in ELISA and capture ELISA. The antibody is specific to dystrophin and does not react with α-actinin and utrophin, an autosomal homologue of dystrophin, also called dystrophin-related protein (DRP).
免疫原
fusion protein containing the C-terminal amino acids of human dystrophine.
應用
Applications in which this antibody has been used successfully, and the associated peer-reviewed papers, are given below.
Immunofluorescence (1 paper)
Western Blotting (1 paper)
Immunofluorescence (1 paper)
Western Blotting (1 paper)
Mouse monoclonal clone MANDRA1 anti-Dystrophin antibody may be used for the localization of dystrophin using various immunochemical assays such as ELISA, capture ELISA, immunoblot, and immunohistochemistry. Monoclonal antibodies against defined regions of dystrophin provide a means for studying its structure and function, interactions with other proteins and the nature of the partial gene products produced in some patients carrying deletions in the dystrophin gene. The antibodies are useful in the prenatal or post-abortion diagnosis of muscular dystrophy carriers by immunohistological analyses.
標靶描述
The C-terminal domain of the human dystrophin molecule (amino acids residues 3558-3684) is present in normal muscle tissue. It is also present in nearly all Becker muscular dystrophies, but is absent in cases of Duchenne muscular dystrophies and in the dystrophic mouse (mdx).
免責聲明
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
13 - Non Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
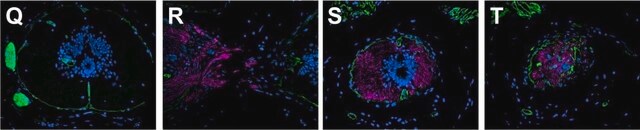
Julia Saifetiarova et al.
Journal of neuroscience research, 95(7), 1373-1390 (2017-04-04)
Bidirectional interactions between neurons and myelinating glial cells result in formation of axonal domains along myelinated fibers. Loss of axonal domains leads to detrimental consequences on nerve structure and function, resulting in reduced conductive properties and the diminished ability to
Kazumi Zushi et al.
Journal of the Japanese Physical Therapy Association = Rigaku ryoho, 15(1), 1-8 (2012-01-01)
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of reloading on atrophied muscle and the time course of hypertrophy and regeneration. Forty-nine male Wistar rats were randomly assigned to groups for hindlimb suspension (HS), hindlimb suspension and reloading
Michelle Goody et al.
PLoS currents, 9 (2017-12-01)
Both genetic and infectious diseases can result in skeletal muscle degeneration, inflammation, pain, and/or weakness. Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the most common congenital muscle disease. DMD causes progressive muscle wasting due to mutations in Dystrophin. Influenza A and B
Tomonari Awaya et al.
PloS one, 7(12), e51638-e51638 (2012-12-14)
Human embryonic stem (ES) cells and induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells are promising sources for the cell therapy of muscle diseases and can serve as powerful experimental tools for skeletal muscle research, provided an effective method to induce skeletal muscle
Rasha Al-Khalidi et al.
Acta neuropathologica communications, 6(1), 27-27 (2018-04-13)
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the most common inherited muscle disorder that causes severe disability and death of young men. This disease is characterized by progressive muscle degeneration aggravated by sterile inflammation and is also associated with cognitive impairment and
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门