推荐产品
應用
人碳酸酐酶 II 已用在研究中对缺血/再灌注体外模型中线粒体和细胞溶质游离锌水平的定量成像进行评估。人类碳酸酐酶 II 也被用于研究用于催化 CO2 水合的新洗涤器概念。
生化/生理作用
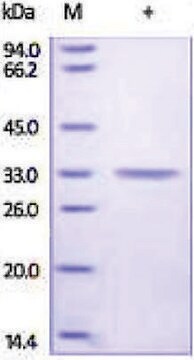
碳酸酐酶是一种锌金属酶,可催化二氧化碳水合为碳酸。它参与重要的生理和病理过程,如pH和CO2稳态、碳酸氢盐和CO2的转运、生物合成反应、骨吸收、钙化和致肿瘤性。它是肾脏酸化所必需的。它的缺乏会导致骨质疏松症、肾小管酸中毒和脑钙化。因此,这种酶是用于青光眼、癫痫和帕金森病临床应用的抑制剂的重要靶点。此外,人们正将它作为肥胖和癌症的潜在目标进行探索。CAII 的分子量约为 30 kDa,主要存在于 II 型肺细胞中。由于这个独特的位置,据推测 CAII 参与肺功能,例如调节液体分泌和促进 CO2 消除。磺胺类药物、氨基磺酸盐和磺胺类药物是 CA 的有效抑制剂。
單位定義
在0 °C条件下,一Wilbur-Anderson (W-A)单位可使0.02M Trizma缓冲液pH在一分钟内从8.3降至 6.3。(一W-A单位基本上相当于一Roughton-Booth单位。)
外觀
以 20 mM Tris、pH 7.5 和 150 mM NaCl 溶液的形式提供。
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
其他客户在看
Samira Ranjbar et al.
International journal of biological macromolecules, 50(4), 910-917 (2012-02-22)
This study reports the interaction between furosemide and human carbonic anhydrase II (hCA II) using fluorescence, UV-vis and circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. Fluorescence data indicated that furosemide quenches the intrinsic fluorescence of the enzyme via a static mechanism and hydrogen
Bryan J McCranor et al.
Journal of bioenergetics and biomembranes, 44(2), 253-263 (2012-03-21)
The role of zinc ion in cytotoxicity following ischemic stroke, prolonged status epilepticus, and traumatic brain injury remains controversial, but likely is the result of mitochondrial dysfunction. We describe an excitation ratiometric fluorescence biosensor based on human carbonic anhydrase II
New scrubber concept for catalytic CO2 hydration by immobilized carbonic anhydrase II and in-situ inhibitor removal in three-phase monolith slurry reactor
Iliuta, I. and F. Larachi
Separation and Purification Technology, 86, 199-214 (2012)
John J Desmarais et al.
Nature microbiology, 4(12), 2204-2215 (2019-08-14)
Bacterial autotrophs often rely on CO2 concentrating mechanisms (CCMs) to assimilate carbon. Although many CCM proteins have been identified, a systematic screen of the components of CCMs is lacking. Here, we performed a genome-wide barcoded transposon screen to identify essential
Screening and docking studies of natural phenolic inhibitors of carbonic anhydrase II
Huang HQ, et al.
Science in China. Series B, Chemistry, Life Sciences & Earth Sciences, 52(3), 332-337 (2009)
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门