所有图片(3)
About This Item
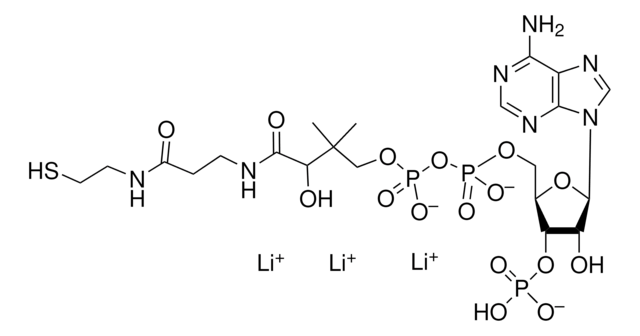
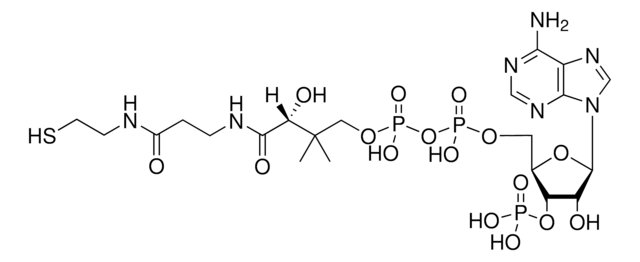
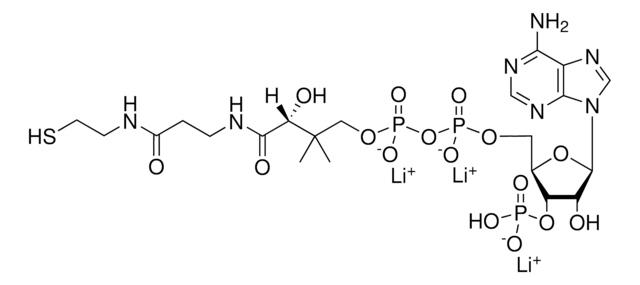
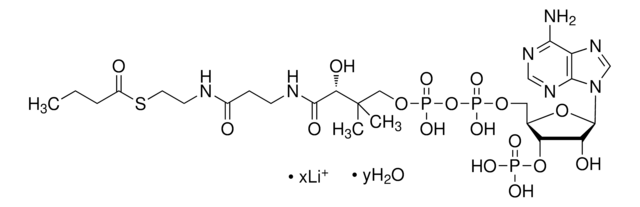
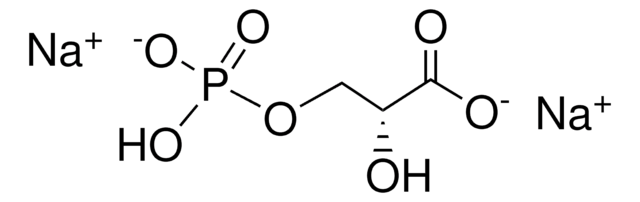
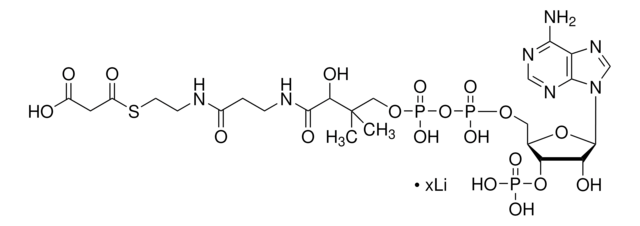
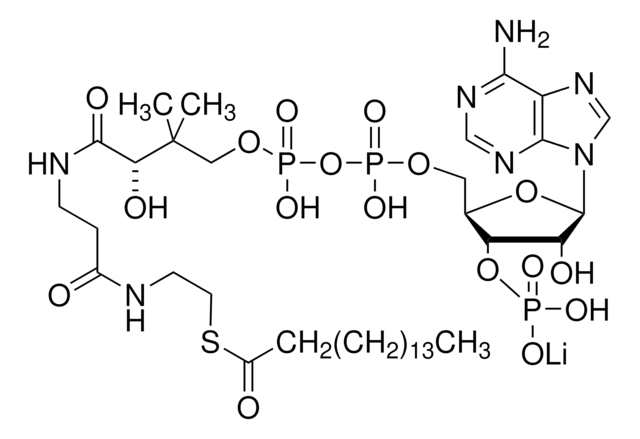
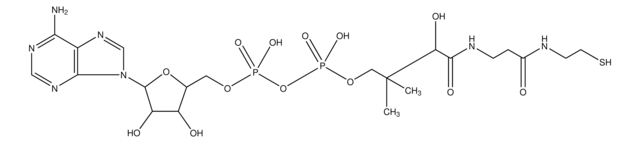
经验公式(希尔记法):
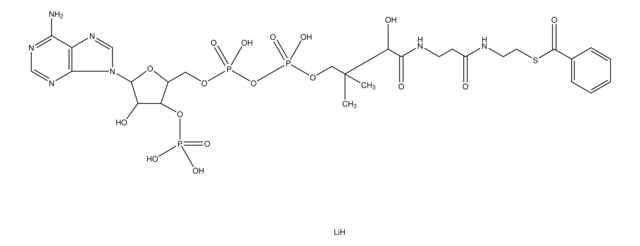
C21H36N7O16P3S · xH2O
CAS号:
分子量:
767.53 (anhydrous basis)
Beilstein:
77809
MDL號碼:
分類程式碼代碼:
12352100
PubChem物質ID:
NACRES:
NA.21
推荐产品
生物源
yeast
品質等級
化驗
≥85% (UV, HPLC)
形狀
powder
官能基
phospholipid
運輸包裝
ambient
儲存溫度
−20°C
SMILES 字串
O.CC(C)(COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1OP(O)(O)=O)n2cnc3c(N)ncnc23)[C@@H](O)C(=O)NCCC(=O)NCCS
InChI
1S/C21H36N7O16P3S.H2O/c1-21(2,16(31)19(32)24-4-3-12(29)23-5-6-48)8-41-47(38,39)44-46(36,37)40-7-11-15(43-45(33,34)35)14(30)20(42-11)28-10-27-13-17(22)25-9-26-18(13)28;/h9-11,14-16,20,30-31,48H,3-8H2,1-2H3,(H,23,29)(H,24,32)(H,36,37)(H,38,39)(H2,22,25,26)(H2,33,34,35);1H2/t11-,14-,15-,16+,20-;/m1./s1
InChI 密鑰
TVSAELAFGDOPKI-BLPRJPCASA-N
應用
辅酶A水合物已用于中华绒螯蟹体内重组乙酰乙酰辅酶A硫解酶(rACAT)的硫解酶测定。它可以用作拉曼光谱测定中的参考标准品。
生化/生理作用
辅酶A(CoA)是由半胱氨酸、泛酸和ATP合成的必需代谢辅助因子。CoA在许多代谢途径中起重要作用,包括三羧酸循环,以及脂肪酸的合成和氧化。CoA的主要功能之一是酰基的携带和转移。酰化衍生物,例如乙酰-CoA,是许多代谢反应中的关键中间体。在饥饿期间以及癌症、糖尿病和酗酒等条件下,CoA水平可能会发生变化。
注意
游离酸不如钠盐或锂盐稳定;在−80 °C下储存时,6个月内会发生5%的分解。
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
其他客户在看
Takuya Ishibashi et al.
Extremophiles : life under extreme conditions, 16(6), 819-828 (2012-09-04)
We have previously reported that the majority of the archaea utilize a novel pathway for coenzyme A biosynthesis (CoA). Bacteria/eukaryotes commonly use pantothenate synthetase and pantothenate kinase to convert pantoate to 4'-phosphopantothenate. However, in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis, two
Francis McCoy et al.
Molecular cell, 52(3), 325-339 (2013-10-08)
Active metabolism regulates oocyte cell death via calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII)-mediated phosphorylation of caspase-2, but the link between metabolic activity and CaMKII is poorly understood. Here we identify coenzyme A (CoA) as the key metabolic signal that inhibits Xenopus
Johannes Holert et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 195(3), 585-595 (2012-12-04)
Bacterial degradation of steroids is widespread, but the metabolic pathways have rarely been explored. Previous studies with Pseudomonas sp. strain Chol1 and the C(24) steroid cholate have shown that cholate degradation proceeds via oxidation of the A ring, followed by
Clonorchis sinensis acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase: identification and characterization of its potential role in surviving in the bile duct
Lin J, et al.
Parasites & vectors, 8(1), 125-125 (2015)
John C Newman et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 287(51), 42436-42443 (2012-10-23)
The sirtuins are a family of NAD(+)-dependent protein deacetylases that regulate cell survival, metabolism, and longevity. Three sirtuins, SIRT3-5, localize to mitochondria. Expression of SIRT3 is selectively activated during fasting and calorie restriction. SIRT3 regulates the acetylation level and enzymatic
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门