492018
NP-40 Alternative, PROTEIN GRADE® Detergent, 10% Solution, Sterile-Filtered
A non-ionic surfactant useful for the isolation and purification of functional membrane protein complexes. This detergent has been purified to reduce levels of contaminating aldehydes, metals, peroxides, and salts.
别名:
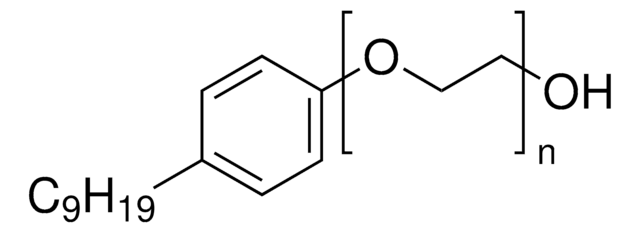
Nonylphenyl Polyethylene Glycol
登录查看公司和协议定价
所有图片(1)
About This Item
推荐产品
品質等級
形狀
solution
製造商/商標名
Calbiochem®
儲存條件
OK to freeze
雜質
≤200 μM Aldehyde
≤200 μM peroxide
顏色
clear colorless
傅導性
≤50 μmho
CMC
50 - 300 μM
運輸包裝
ambient
儲存溫度
2-8°C
InChI
1S/C19H32O3/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-18-10-12-19(13-11-18)22-17-16-21-15-14-20/h10-13,20H,2-9,14-17H2,1H3
InChI 密鑰
BLXVTZPGEOGTGG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
一般說明
A non-ionic surfactant used in the isolation and purification of functional membrane protein complexes and in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2DGE). Similar in usage to NP-40 and TRITON™ X-100 (Cat. No. 648462). Purified to reduce levels of contaminating aldehydes, metals, peroxides, and salts. CMC: 50-300 µM.
A non-ionic surfactant useful for the isolation and purification of functional membrane protein complexes. This detergent has been purified to reduce levels of contaminating aldehydes, metals, peroxides, and salts.
警告
Toxicity: Irritant (B)
外觀
10% aqueous solution.
重構
Following initial use, aliquot and freeze (-20°C).
其他說明
Ripoche, P., et al. 1982. Biochim. Biophys. Acta693, 497.
法律資訊
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
PROTEIN GRADE is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Triton is a trademark of The Dow Chemical Company or an affiliated company of Dow
訊號詞
Warning
危險聲明
危險分類
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
其他客户在看
Tsung-Han S Hsieh et al.
Molecular cell, 78(3), 539-553 (2020-03-28)
Whereas folding of genomes at the large scale of epigenomic compartments and topologically associating domains (TADs) is now relatively well understood, how chromatin is folded at finer scales remains largely unexplored in mammals. Here, we overcome some limitations of conventional
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门