Myosin
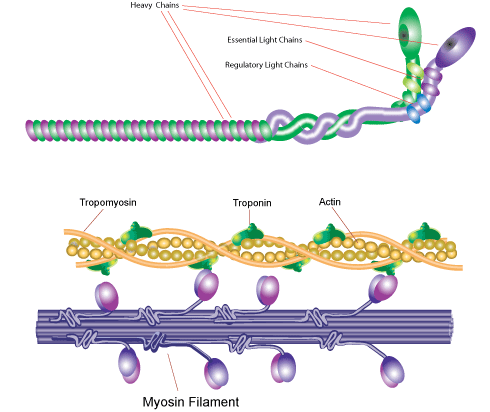
Myosins are a family of ATP-dependent motor proteins. Myosin II is the major contractile protein involved in eukaryotic muscle contraction by "walking" along actin microfilaments of the sarcomere. Each of the heavy chains has a globular head region for ATP hydrolysis and actin binding and tail region. Myosins are typically composed one or two heavy chains and four or more light chains. In Myosin II the heavy chain exists as a dimmer and contains two regulatory and two essential light chains bound to each heavy chain. Myosin light chains can resemble calmodulin and may also bind calcium.
Materials
Loading
Zaloguj się, aby kontynuować
Zaloguj się lub utwórz konto, aby kontynuować.
Nie masz konta użytkownika?