SAE0020
Cellulase, enzyme blend
Synonym(s):
Cellic CTec2
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
General description
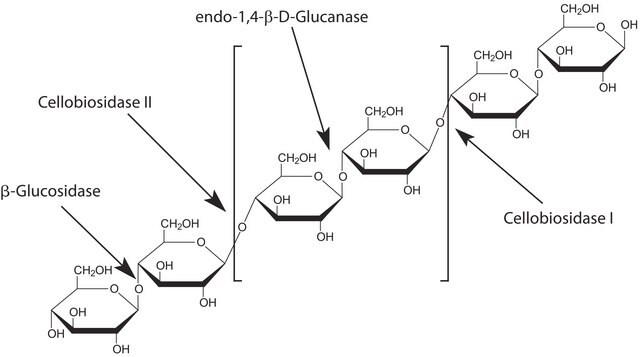
Cellulase is a member of glycoside hydrolase family and is produced by a number of cellulolytic microbes.
This product contains cellulases, ß-glucosidases, and hemicellulase, for the application of degrading cellulose to fermentable sugars. This product is effective on a wide variety of pre-treated lignocellulosic bimass materials, for converting the carbohydrates in these materials into simple sugars prior to fermentation, for application in biofuels research.
Application
Cellulase, enzyme blend has been used for the purpose of enzymatic hydrolysis.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cellulase is responsible for the breakdown of insoluble plant polymer cellulosic substrates into soluble sugars, mostly cellobiose and glucose. It specifically catalyzes the hydrolysis of β -1,4 glucosidic bonds in cellulose. Animals do not naturally possess the ability to digest cellulose, but do so with the help of gut microorganisms.
Legal Information
A product of Novozyme Corp
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Liwen He et al.
Bioresource technology, 289, 121693-121693 (2019-07-02)
The optimum condition of steam explosion pretreatment was screened for hippophae, and anaerobic calcium oxide (CaO) alkalization was further used to improve its enzymatic hydrolysis. Steam-exploded hippophae reached the lowest pH value (4.01) and the maximal hemicellulose removal (77.16%) at
A cellulase gene of termite origin.
Watanabe H, et al.
Nature, 394(6691), 330-330 (1998)
Model of acetic acid-affected growth and poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) production by Cupriavidus necator DSM 545.
Marudkla J, et al.
Journal of Biotechnology, 268, 12-20 (2018)
Liwen He et al.
Bioresource technology, 298, 122510-122510 (2019-12-15)
A better understanding of biomass usability during storage would offer basis for management decisions in production. High-moisture corn stover was ensiled with sulfuric acid (H2SO4, 0.3% and 0.6%) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH, 0.5% and 1.0%) and ensiling characteristics, lignocellulosic profile
Qiulu Chu et al.
Biotechnology for biofuels, 14(1), 136-136 (2021-06-14)
Ethanol organosolv (EOS) pretreatment is one of the most efficient methods for boosting biomass saccharification as it can achieve an efficient fractionation of three major constituents in lignocellulose. However, lignin repolymerization often occurs in acid EOS pretreatment, which impairs subsequent
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service