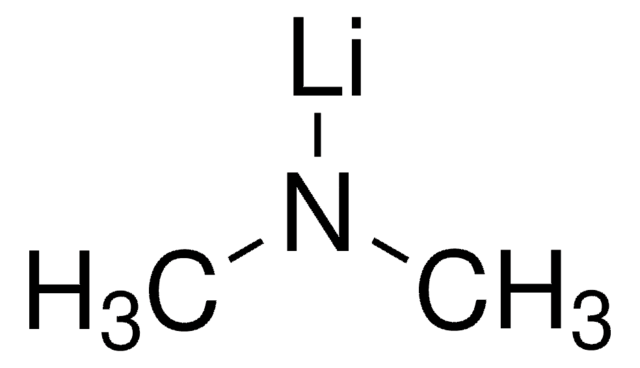
579211
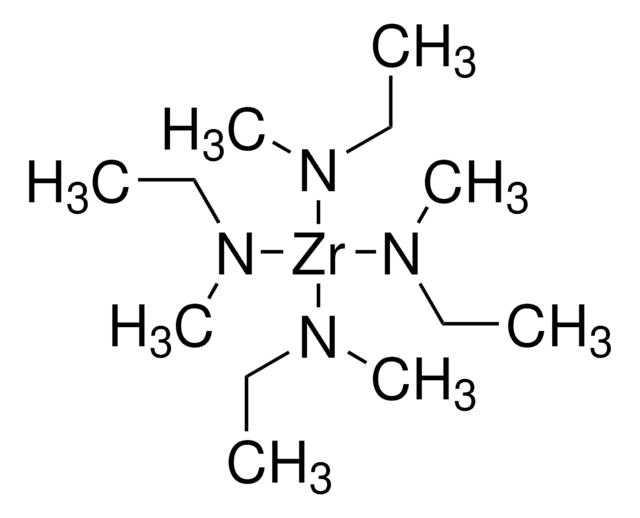
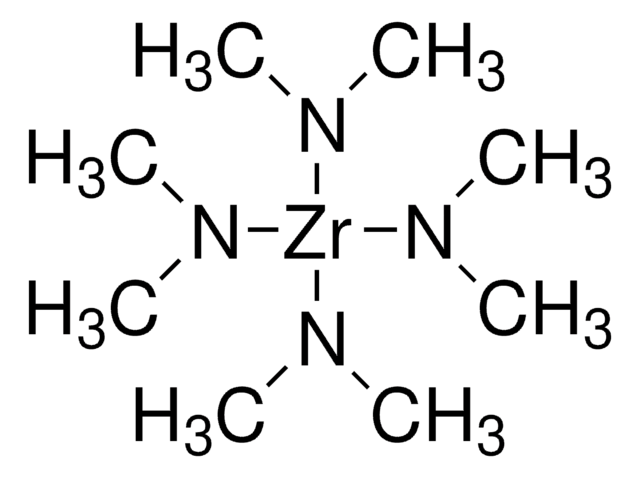
Tetrakis(dimethylamido)zirconium(IV)
electronic grade, ≥99.99% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
TDMAZ, Tetrakis(dimethylamino)zirconium(IV)
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
electronic grade
Assay
≥99.99% trace metals basis
form
solid
reaction suitability
core: zirconium
mp
57-60 °C (lit.)
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
CN(C)[Zr](N(C)C)(N(C)C)N(C)C
InChI
1S/4C2H6N.Zr/c4*1-3-2;/h4*1-2H3;/q4*-1;+4
InChI key
DWCMDRNGBIZOQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Sol. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3 - Water-react 2
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Supplementary Hazards
Storage Class Code
4.3 - Hazardous materials which set free flammable gases upon contact with water
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
No data available
Flash Point(C)
No data available
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
This technical spotlight focuses on the thin film solid oxide fuel cells (TF-SOFC). TF-SOFCs refer to solid oxide fuel cells with electrolyte thin films. This review highlights technical advantages of TF-SOFC and introduces deposition methods of electrolyte thin films to fabricate TF-SOFC.
Since the demonstration of the first practical solar cell 60 years ago, research on novel materials, improved solar cell design and structure, and innovative manufacturing processes have all contributed to a continuous increase in the efficiency of photovoltaic (PV) devices.
A hard disk drive (HDD) is a data storage device that stores digital information by magnetizing nanosized magnets on flat disks and retrieves data by sensing the resulting magnetic field.
Nanomaterials are considered a route to the innovations required for large-scale implementation of renewable energy technologies in society to make our life sustainable.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service