SRP3130
Oncostatin M (209 aa) human
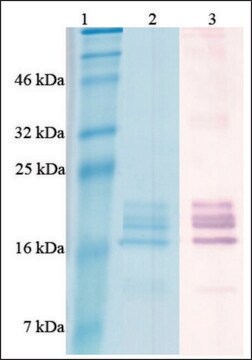
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, ≥98% (SDS-PAGE), ≥98% (HPLC), suitable for cell culture
Synonym(s):
OSM
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352202
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
biological source
human
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Assay
≥98% (HPLC)
≥98% (SDS-PAGE)
form
lyophilized
potency
≤2.0 ng/mL ED50
mol wt
23.9 kDa
packaging
pkg of 10 μg
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
impurities
<0.1 EU/μg endotoxin, tested
color
white to off-white
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
human ... OSM(5008)
General description
Oncostatin M (OSM) is produced by activated T cells, monocytes and Kaposi′s sarcoma cells. OSM shares several structural and functional characteristics with leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF). The human OSM gene encodes for a 252 amino acid polypeptide, containing 25 amino acid signal sequence for secretion and a 227 precursor protein. Proteolytic processing of this precursor removes an 18 amino acid C-terminal peptide and generates the mature OSM form. Human OSM is active on murine cells. Recombinant human Oncostatin M is a 23.9kDa protein, containing 209 amino acid residues.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Oncostatin M (OSM) is a growth and differentiation factor that participates in the regulation of neurogenesis, osteogenesis and hematopoiesis. It can exert both stimulatory and inhibitory effects on cell proliferation. OSM stimulates the proliferation of fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells and Kaposi′s sarcoma cells, but, inhibits the growth of some normal and tumor cell lines. It also promotes cytokine release [e.g. interleukin-6 (IL-6), granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)] from endothelial cells, and enhances the expression of low-density lipoprotein receptor in hepatoma cells.
Sequence
MAAIGSCSKE YRVLLGQLQK QTDLMQDTSR LLDPYIRIQG LDVPKLREHC RERPGAFPSE ETLRGLGRRG FLQTLNATLG CVLHRLADLE QRLPKAQDLE RSGLNIEDLE KLQMARPNIL GLRNNIYCMA QLLDNSDTAE PTKAGRGASQ PPTPTPASDA FQRKLEGCRF LHGYHRFMHS VGRVFSKWGE SPNRSRRHSP HQALRKGVRR
Physical form
Lyophilized from 10 mM Sodium Citrate, pH 4.0.
Reconstitution
Centrifuge the vial prior to opening. Reconstitute in water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/ml. Do not vortex. This solution can be stored at 2-8°C for up to 1 week. For extended storage, it is recommended to further dilute in a buffer containing a carrier protein (example 0.1% BSA) and store in working aliquots at -20°C to -80°C.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Bruce, A.G., et al.
Cytokine Reference, 585-598 (2001)
T M Rose et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 88(19), 8641-8645 (1991-10-01)
Oncostatin M (OSM), a glycoprotein of Mr approximately 28,000 produced by activated monocyte and T-lymphocyte cell lines, was previously identified by its ability to inhibit the growth of cells from melanoma and other solid tumors. We have detected significant similarities
Pulmonary expression of oncostatin M (OSM) promotes inducible BALT formation independently of IL-6, despite a role for IL-6 in OSM-driven pulmonary inflammation.
Botelho FM
Journal of Immunology, 191(3), 1453-1464 (2013)
Oncostatin M and leukemia inhibitory factor do not use the same functional receptor in mice.
Ichihara M
Blood, 90(1), 165-173 (1997)
Oncostatin M stimulates the growth of dermal fibroblasts via a mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway.
Ihn H and Tamaki K
Journal of Immunology, 165(4), 2149-2155 (2000)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service