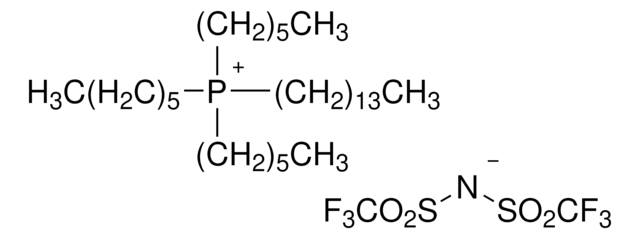50826
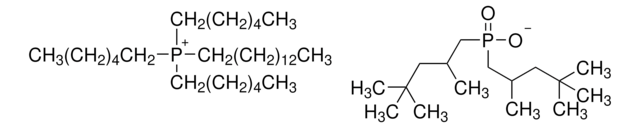
Trihexyltetradecylphosphonium decanoate
≥95.0% (NMR)
Synonym(s):
Tetradecyltrihexylphosphonium decanoate
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
[CH3(CH2)5]3P[OCO(CH2)8CH3](CH2)13CH3
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
655.11
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥95.0% (NMR)
functional group
phosphine
SMILES string
CCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCC[P+](CCCCCC)(CCCCCC)CCCCCC
InChI
1S/C32H68P.C10H20O2/c1-5-9-13-17-18-19-20-21-22-23-24-28-32-33(29-25-14-10-6-2,30-26-15-11-7-3)31-27-16-12-8-4;1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10(11)12/h5-32H2,1-4H3;2-9H2,1H3,(H,11,12)/q+1;/p-1
InChI key
HQIPXXNWLGIFAY-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Related Categories
General description
Trihexyltetradecylphosphonium decanoate is an ionic liquid that is used as a convenient and efficient solvent for a wide range of chemical reactions due to its unique properties such as its high thermal stability and low volatility, which make it useful in a variety of organic synthesis applications.
Application
Trihexyltetradecylphosphonium decanoate can be used as a demulsifying agent due to its unique solubility and surface-active properties. It is also used as a catalyst in Henry nitroaldol reactions.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class Code
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Mohammad Abdul Sattar et al.
ACS omega, 5(33), 21191-21202 (2020-09-03)
Intermolecular interactions between the constituents of a polymer nanocomposite at the polymer-particle interface strongly affect the segmental mobility of polymer chains, correlated with their glass transition behavior, and are responsible for the improved dynamical viscoelastic properties. In this work, we
Sarah F R Taylor et al.
Physical chemistry chemical physics : PCCP, 19(22), 14306-14318 (2017-05-26)
This study reports on understanding the formation of bubbles in ionic liquids (ILs), with a view to utilising ILs more efficiently in gas capture processes. In particular, the impact of the IL structure on the bubble sizes obtained has been
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service