MABE1084
Anti-Topoisomerase I-DNA Covalent Complexes Antibody, clone 1.1A
clone 1.1A, from mouse
Synonym(s):
Topoisomerase I-DNA covalent complex, DNA topoisomerase 1-DNA covalent complex, Topo I-DNA covalent complex, TopoI cc, TopoIcc
About This Item
ELISA
FACS
ICC
dot blot: suitable
flow cytometry: suitable
immunocytochemistry: suitable
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
antibody form
purified antibody
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
1.1A, monoclonal
species reactivity
human, mouse
technique(s)
ELISA: suitable
dot blot: suitable
flow cytometry: suitable
immunocytochemistry: suitable
isotype
IgG2bκ
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
wet ice
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... TOP1(7150)
General description
Specificity
Immunogen
Application
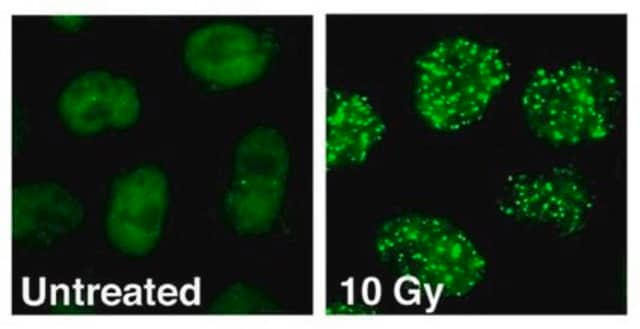
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: 10 µg/mL from a representative lot detected topoisomerase I/DNA covalent complexes in Topotecan-treated A549 human lung carcinoma cells (Courtesy of Dr. Scott H. Kaufmann, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN).
Flow Cytometry Analysis: 10 µg/mL from a representative lot detected topoisomerase I/DNA covalent complexes in Topotecan-treated HCT116 human colon cancer cells (Courtesy of Dr. Scott H. Kaufmann, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN).
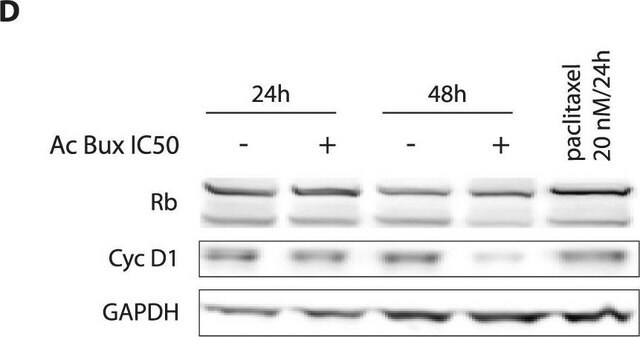
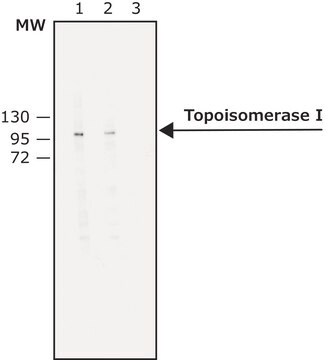
Dot Blot Analysis: A representative lot detected the Topotecan-/TPT-stablized topoisomerase I/DNA covalent complexes, but not free topoisomerase I (non-DNA complexed) by slot blot using CsCl2 gradient-fractionated lysates from TPT-treated and untreated A549 cells (Patel, A.G., et al, (2016). 44(6):2816-2826).
Dot Blot Analysis: A representative lot detected a Topotecan (TPT) dose-dependent increase of TPT-stabilized topoisomerase I/DNA covalent complexes in lysates from TPT-treated A549 and HCT116 cells by slot blot (Patel, A.G., et al, (2016). 44(6):2816-2826).
Dot Blot Analysis: A representative lot detected stabilized topoisomerase I/DNA covalent complexes in lysates from A549 cells treated with Camptothecins (CPT, SN-38, TPT) or Indenoisoquinolines (NSC 314622, NSC 725776, NSC 743400), but not nucleoside analogues (cytarabine and gemcitabine) (Patel, A.G., et al, (2016). 44(6):2816-2826).
ELISA Analysis: A representative lot detected the immunogen peptide corresponding to topoisomerase I active site sequence with phosphorylated Tyr723, but not the peptide with non-phosphorylated Tyr273 by direct (non-sandwich) ELISA (Patel, A.G., et al, (2016). 44(6):2816-2826).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected a dose-dependent increase of non-nucleolar topoisomerase I/DNA covalent complex loci in Topotecan-/TPT-treated A549 cells, while the small number of loci in untreated cells were seen only in nucleoli (Patel, A.G., et al, (2016). 44(6):2816-2826).
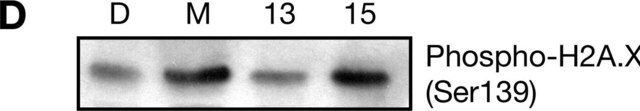
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected a temporally and spatially distinct nuclear loci formation of topoisomerase I/DNA covalent complexes from those of phospho-H2AX and Rad51 in Topotecan-/TPT-treated A549 cells (Patel, A.G., et al, (2016). 44(6):2816-2826).
Epigenetics & Nuclear Function
Chromatin Biology
Quality
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: 10 µg/mL of this antibody detected topoisomerase I/DNA covalent complexes in Topotecan-treated A549 human lung carcinoma cells.
Target description
Physical form
Storage and Stability
Other Notes
Disclaimer
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service