ABE2854
Anti-Histone H3K27butyrl
Sinónimos:
H3K27butyrl
About This Item
Productos recomendados
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
antibody form
purified antibody
antibody product type
primary antibodies
mol wt
calculated mol wt 15.4 kDa
observed mol wt ~17 kDa
purified by
affinity chromatography
species reactivity
human, mouse
packaging
antibody small pack of 100 μL
technique(s)
ChIP: suitable
dot blot: suitable
immunofluorescence: suitable
western blot: suitable
isotype
IgG
epitope sequence
N-terminal half
Protein ID accession no.
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
2-8°C
Specificity
Immunogen
Application
Evaluated by Western Blotting in lysates from HCT-116 cells treated with 5 mM Sodium butyrate.
Western Blotting Analysis: A 1:1,000 dilution of this antibody detected Histone H3 butyrlated on lysine 27 in lysate from HCT-116 cells treated with 5 mM Sodium butyrate.
Tested Applications
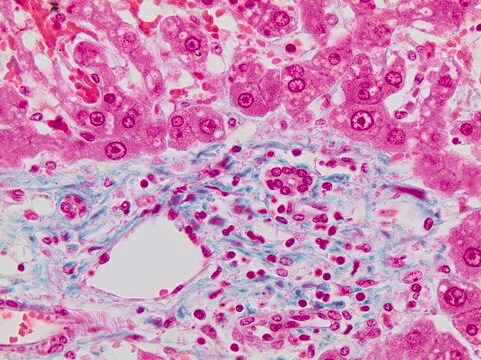
Immunofluorescence Analysis: A 1:500 dilution from a representative lot detected Histone H3K27butyrl in Mouse cecal sections (Data courtesy of Dr. Leah Gates, Dave Allis Lab @ Rockefeller University, New York).
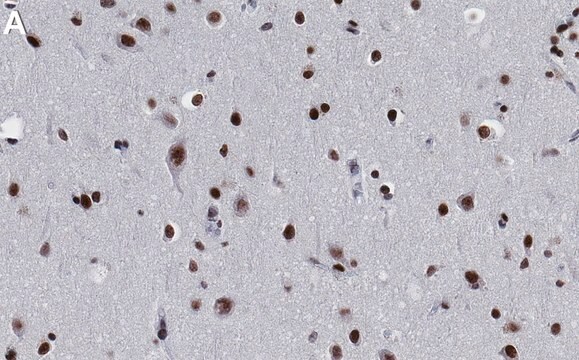
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Analysis: 10 µg from a representative lot detected Histone H3K27butyrl in HCT-116 cells (Data courtesy of Dr. Leah Gates, Dave Allis Lab @ Rockefeller University, New York).
Dot Blot: A 1:2,000 dilution from a representative lot detected Histone H3K27butyrl peptide (Data courtesy of Dr. Leah Gates, Dave Allis Lab @ Rockefeller University, New York).
Note: Actual optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user as specimens, and experimental conditions may vary with the end user.
Target description
Physical form
Reconstitution
Storage and Stability
Other Notes
Disclaimer
¿No encuentra el producto adecuado?
Pruebe nuestro Herramienta de selección de productos.
Storage Class
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico