70664
Benzonase® Nuclease
Purity > 99%, Effective viscosity reduction and removal of nucleic acids from protein solutions
Synonym(s):
Endonuclease from Serratia marcescens
About This Item
Recommended Products
product name
Benzonase® Nuclease, Purity > 99%, Effective viscosity reduction and removal of nucleic acids from protein solutions
biological source
Serratia marcescens
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Assay
>99% (SDS-PAGE)
form
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
manufacturer/tradename
Novagen®
storage condition
OK to freeze
concentration
25-29 units/μL
impurities
<0.25 EU/kU Total endotoxin
application(s)
research use
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
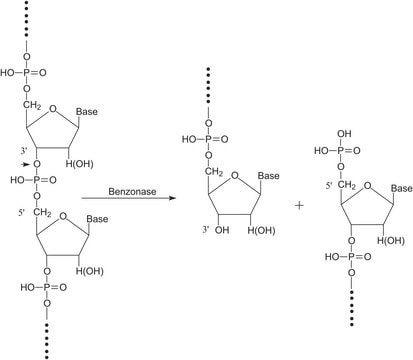
The enzyme consists of two subunits of30 kDa each. It is functional between pH 6 and 10 and from 0-42°C and requires1-2 mM Mg2+ for activation. The enzyme is also active in the presence of ionic and non-ionic detergents, reducing agents, PMSF(1 mM), EDTA (1 mM) and urea (relative activity depends on specific conditions).Activity is inhibited by > 150 mM monovalent cations, > 100 mM phosphate, > 100 mMammonium sulfate, or > 100 mM guanidine HCl.
Benzonase Nuclease is available in ultrapure (> 99% by SDS-PAGE) and pure (> 90%) grades at a standard concentration of 25-29 U/µl and at a high concentration (HC) of 250 U/µl. Both preparations are free of detectable protease and have specific activity> 1 × 106 U/mg protein. The > 99% purity grade is tested for endotoxins and contains< 0.25 EU/1000 units. The product is supplied in 50% glycerol. Store at -20°C.

Total endotoxin:< 0.25 EU/1,000 units. Purity: > 99% by SDS-PAGE.
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Warning
Unit Definition
Legal Information
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service