D5319
Deoxyribonuclease I bovine
recombinant, expressed in Pichia pastoris, buffered aqueous glycerol solution, ≥5,000 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
DNAse I, Deoxyribonucleate 5′-oligonucleotido-hydrolase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
biological source
bovine
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in Pichia pastoris
Assay
≥95%
form
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
specific activity
≥5,000 units/mg protein
mol wt
~39 kDa
technique(s)
DNA extraction: suitable
suitability
suitable for molecular biology
application(s)
diagnostic assay manufacturing
foreign activity
RNAse and protease, free
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
DNAse I from Sigma was used to treat nuclear lysate to obtain single nucleosomes in a study. The enzyme has also been for the preparation and harvest of mice mammary glands.
Deoxyribonuclease I bovine has been used in a study to compare the initial actions of spleen deoxyribonuclease and pancreatic deoxyribonuclease. Deoxyribonuclease I bovine has also been used in a study to investigate deoxythymidine 3′, 5′-di-p-nitrophenyl phosphate as a synthetic substrate for bovine pancreatic deoxyribonuclease.
Used for the removal of DNA from protein samples.
Biochem/physiol Actions
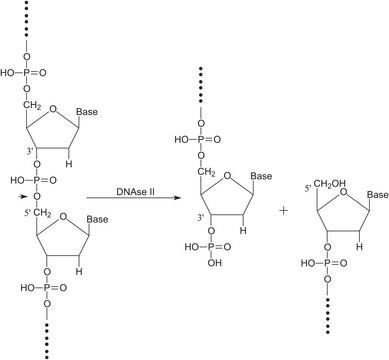
DNase I is an endonuclease that acts on phosphodiester bonds (adjacent to pyrimidines) to produce polynucleotides with terminal 5′-phosphates. The pH optimum is found to be between 7 and 8. Divalent cations such as Mn2+, Ca2+, Co2+, and Zn2+ are activators of the enzyme. A concentration of 5 mM Ca2+ stabilizes the enzyme against proteolytic digestion. 2-Mercaptoethanol, chelators, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and actin are known to inhibit the enzyme activity.
Digests single- and double-stranded DNA to a mixture of mono- and oligonucleotides carrying 5′ phosphates and 3′ OH termini. This catalytic activity is divalent ion-dependent. In the presence of Mg2+, DNase I hydrolyzes each strand of double-stranded DNA randomly and independently. In the presence of Mn2+, both strands can be cleaved.
Features and Benefits
- RNA purification by removing DNA
- Prepare DNA for nick translation1
- Footprinting assays to determine DNA-protein interactions2
Unit Definition
One unit will produce a ΔA260 of 0.001 per min per mL reaction mixture using calf thymus DNA at pH 5.0 and 25°C
Physical form
Supplied as a solution in 4 mg/ml glycine pH 5.0, 5 mM calcium acetate and 50% glycerol
Preparation Note
Produced without using any animal cells or animal derived materials.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Wendy A Kellner et al.
Nucleic acids research, 41(20), 9274-9283 (2013-08-16)
Brd4 is a double bromodomain protein that has been shown to interact with acetylated histones to regulate transcription by recruiting Positive Transcription Elongation Factor b to the promoter region. Brd4 is also involved in gene bookmarking during mitosis and is
Alice S Kaanta et al.
Breast cancer research : BCR, 15(4), R65-R65 (2013-08-21)
The mouse mammary gland provides a powerful model system for studying processes involved in epithelial tissue development. Although markers that enrich for mammary stem cells and progenitors have been identified, our understanding of the mammary developmental hierarchy remains incomplete. We
Properties of chromatographically purified bovine pancreatic deoxyribonuclease.
P A Price et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 244(3), 917-923 (1969-02-10)
Gregory Heller et al.
BMC plant biology, 8, 19-19 (2008-02-27)
Symbiotic ectomycorrhizal associations of fungi with forest trees play important and economically significant roles in the nutrition, growth and health of boreal forest trees, as well as in nutrient cycling. The ecology and physiology of ectomycorrhizal associations with Pinus sp
Vonda Cummings et al.
PloS one, 6(1), e16069-e16069 (2011-01-20)
Ocean acidification is a well recognised threat to marine ecosystems. High latitude regions are predicted to be particularly affected due to cold waters and naturally low carbonate saturation levels. This is of concern for organisms utilising calcium carbonate (CaCO(3)) to
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service