R4642
Ribonuclease A from bovine pancreas
(Solution of 50% glycerol, 10mM Tris-HCL pH 8.0)
Synonym(s):
Pancreatic Ribonuclease, RNAsea, RNase A, Ribonucleate 3′-pyrimidinooligonucleotidohydrolase
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
bovine pancreas
Quality Level
grade
for molecular biology
form
(Solution of 50% glycerol, 10mM Tris-HCL pH 8.0)
mol wt
13.7 kDa
~13,700
concentration
20-40 mg/mL
suitability
suitable for
foreign activity
Endonuclease and exonuclease, none detected
NICKase and DNase, none detected
storage temp.
−20°C
InChI
1S/C9H14N4O3/c10-2-1-8(14)13-7(9(15)16)3-6-4-11-5-12-6/h4-5,7H,1-3,10H2,(H,11,12)(H,13,14)(H,15,16)
InChI key
CQOVPNPJLQNMDC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
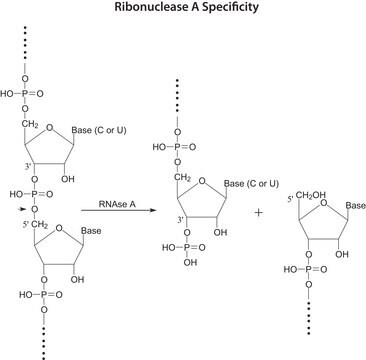
- RNase A is used to remove RNA from DNA plasmid and genomic DNA preparations and protein samples.
- RNase A is also used in RNA sequence analysis and protection assays.
- RNase A has been used as a tool for computer-aided drug design.
- RNase A supports the analysis of RNA sequences.
- RNase A hydrolyze RNA contained in protein samples.
- Purification of DNA is supported by RNase A.
- RNase protection assays
- Removal of unspecifically bound RNA
- Analysis of RNA sequences
- Hydrolysis of RNA contained in protein samples
- Plasmid DNA purification
Features and Benefits
Components
Unit Definition
Boiling stock solutions of this RNase A product to inactivate residual DNase is not necessary and may cause precipitation of RNase and possible loss of enzymatic activity. If an RNase A solution is heated at a neutral pH, precipitation will occur. When heated at a lower pH, some precipitation may occur because of protein impurities that are present.
Analysis Note
Other Notes
Application
inhibitor
related product
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Available Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) procedures, reagents and equipment.
Separation of Ribonuclease A from bovine pancreas, Type I-A, powder, ≥60% RNase A basis (SDS-PAGE), ≥50 Kunitz units/mg protein; α-Chymotrypsinogen A from bovine pancreas, essentially salt-free, lyophilized powder; Cytochrome c from bovine heart, ≥95% based on Mol. Wt. 12,327 basis; Lysozyme from chicken egg white, lyophilized powder, protein ≥90 %, ≥40,000 units/mg protein
Separation of Ribonuclease A from bovine pancreas, Type I-A, powder, ≥60% RNase A basis (SDS-PAGE), ≥50 Kunitz units/mg protein; α-Chymotrypsinogen A from bovine pancreas, essentially salt-free, lyophilized powder; Cytochrome c from bovine heart, ≥95% based on Mol. Wt. 12,327 basis; Lysozyme from chicken egg white, lyophilized powder, protein ≥90 %, ≥40,000 units/mg protein
Separation of Ribonuclease A from bovine pancreas, Type I-A, powder, ≥60% RNase A basis (SDS-PAGE), ≥50 Kunitz units/mg protein; α-Chymotrypsinogen A from bovine pancreas, essentially salt-free, lyophilized powder; Cytochrome c from bovine heart, ≥95% based on Mol. Wt. 12,327 basis; Lysozyme from chicken egg white, lyophilized powder, protein ≥90 %, ≥40,000 units/mg protein
Protocols
This protocol describes a simple and convenient procedure to isolate pure DNA from a variety of plant species using the GenElute Plant Genomic DNA Miniprep Kit.
This procedure may be used for determination of Ribonuclease A (RNase A) activity.
Chromatograms
application for HPLCOur team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service