추천 제품
Quality Level
분석
≥90%
저장 온도
−20°C
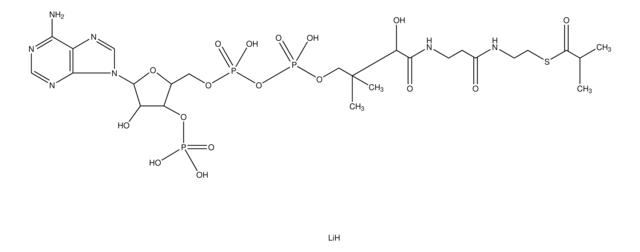
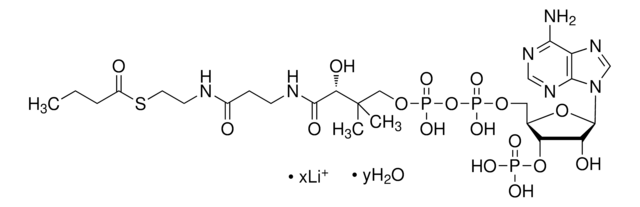
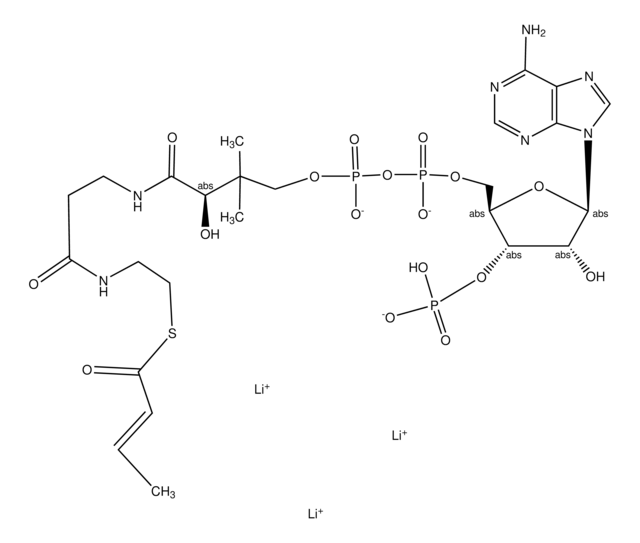
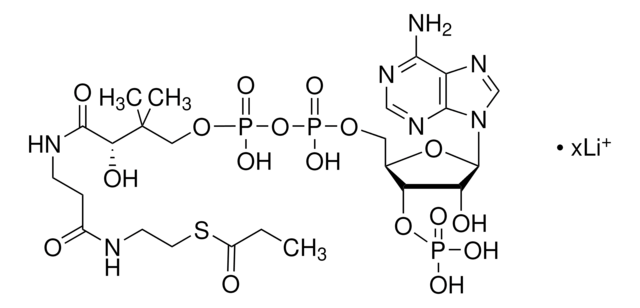
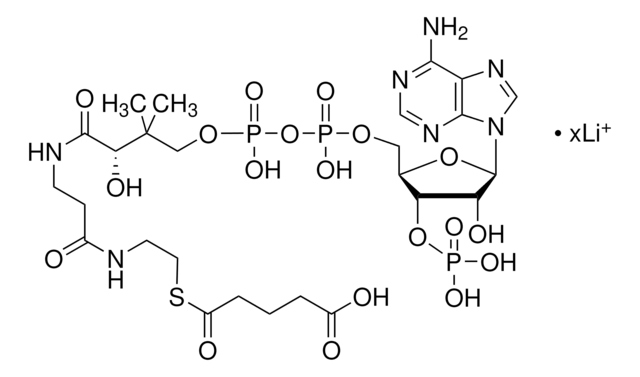
SMILES string
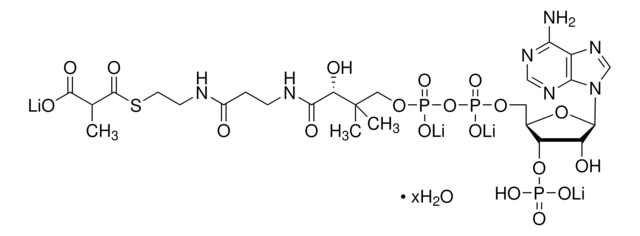
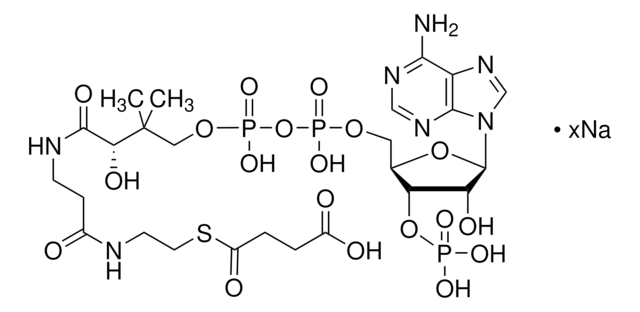
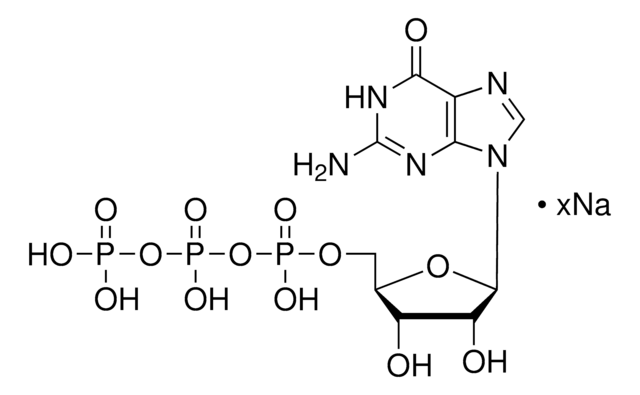
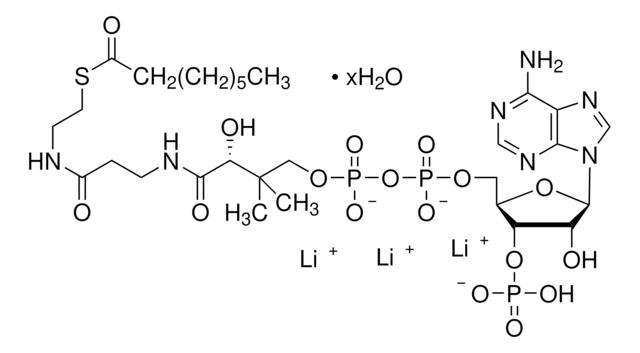
[Li+].[Li+].[Li+].[H]O[H].CC(C)CC(=O)SCCNC(=O)CCNC(=O)[C@H](O)C(C)(C)COP([O-])(=O)OP([O-])(=O)OC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1OP(O)([O-])=O)n2cnc3c(N)ncnc23
InChI
1S/C26H44N7O17P3S.3Li.H2O/c1-14(2)9-17(35)54-8-7-28-16(34)5-6-29-24(38)21(37)26(3,4)11-47-53(44,45)50-52(42,43)46-10-15-20(49-51(39,40)41)19(36)25(48-15)33-13-32-18-22(27)30-12-31-23(18)33;;;;/h12-15,19-21,25,36-37H,5-11H2,1-4H3,(H,28,34)(H,29,38)(H,42,43)(H,44,45)(H2,27,30,31)(H2,39,40,41);;;;1H2/q;3*+1;/p-3/t15-,19-,20-,21+,25-;;;;/m1..../s1
InChI key
RABPIYFVNICBEC-YVBWDKSKSA-K
일반 설명
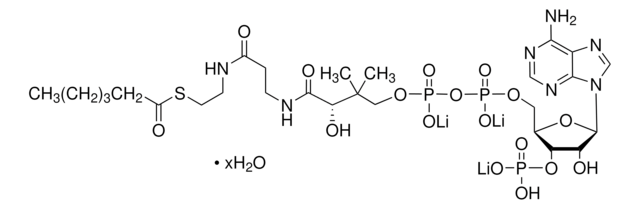
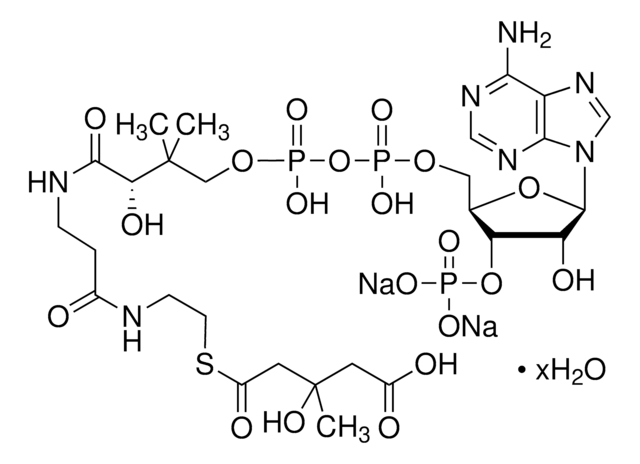
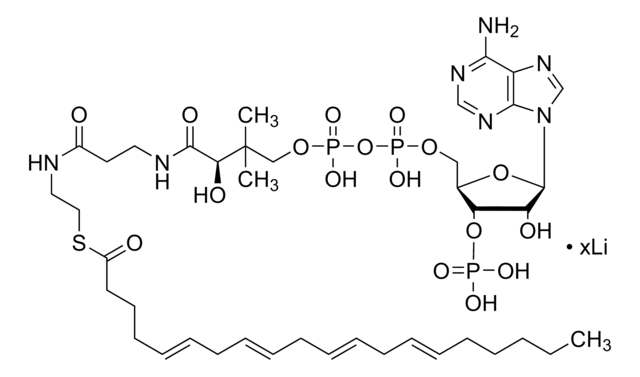
Isovaleryl coenzyme A is an intermediate in leucine catabolism. Iv-CoA is synthesized from β-methylbutyric acid by the action of enzyme acyl CoA synthetase. The conversion of isovaleryl-CoA to methylcrotonyl-CoA is catalyzed by the enzyme isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase in leucine catabolism pathway. The enzyme isovaleryl-CoA oxidase also calalyzes this conversion in fatty acid β-oxidation pathway.
애플리케이션
Isovaleryl coenzyme A (IV-CoA ) lithium salt hydrate may be used:
- as substrate for β-Hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid synthesis in cell-free extracts from G. reessii
- in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the characterization of IV-CoA from lymphocytes
- as a substrate in isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase assay
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
개인 보호 장비
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
이미 열람한 고객
Tobias Bock et al.
Nucleic acids research, 45(4), 2166-2178 (2016-12-13)
Isovaleryl coenzyme A (IV-CoA) is an important building block of iso-fatty acids. In myxobacteria, IV-CoA is essential for the formation of signaling molecules involved in fruiting body formation. Leucine degradation is the common source of IV-CoA, but a second, de
Lee et al.
Archives of microbiology, 169(3), 257-262 (1998-03-28)
Galactomyces reessii accomplishes the enzymatic transformation of beta-methylbutyric acid (isovaleric acid) to beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyric acid. The enzymatic basis for this bioconversion was evaluated by analyzing cell-free extracts of G. reessii for enzyme activities commonly associated with leucine catabolism. G. reessii extracts
A biosynthetic pathway to isovaleryl-CoA in myxobacteria: the involvement of the mevalonate pathway.
Taifo Mahmud et al.
Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology, 6(2), 322-330 (2004-12-28)
A biosynthetic shunt pathway branching from the mevalonate pathway and providing starter units for branched-chain fatty acid and secondary metabolite biosynthesis has been identified in strains of the myxobacterium Stigmatella aurantiaca. This pathway is upregulated when the branched-chain alpha-keto acid
Helge B Bode et al.
Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology, 10(1), 128-140 (2008-10-11)
Isovaleryl-CoA (IV-CoA) is usually derived from the degradation of leucine by using the Bkd (branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase) complex. We have previously identified an alternative pathway for IV-CoA formation in myxobacteria that branches from the well-known mevalonate-dependent isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway.
Helge B Bode et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 188(18), 6524-6528 (2006-09-06)
Isovaleryl-coenzyme A (IV-CoA) is the starting unit for some secondary metabolites and iso-odd fatty acids in several bacteria. According to textbook biochemistry, IV-CoA is derived from leucine degradation, but recently an alternative pathway that branches from the well-known mevalonate-dependent isoprenoid
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.