추천 제품
product name
Epidermal Growth Factor from mouse, EGF
생물학적 소스
mouse
Quality Level
재조합
expressed in E. coli
분석
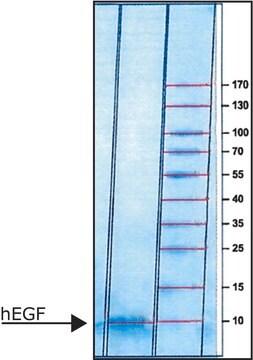
≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
형태
lyophilized powder
효능
0.05-1 ng/mL ED50/EC50
분자량
~6 kDa
포장
pkg of 100 μg
저장 조건
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
기술
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
불순물
≤1 EU/μg endotoxin (Protein)
색상
white
solubility
water: soluble 0.10 mL, clear, colorless
UniProt 수납 번호
저장 온도
−20°C
유전자 정보
mouse ... Egf(13645)
일반 설명
Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a small mitogenic polypeptide (∼6kDa) present in many mammalian species and distributed throughout a wide number of tissues and body fluids. Four ErbB (HER) family receptor tyrosine kinases, including EGFR/ErbB1, ErbB2, ErbB3, and ErbB4 mediate responses to EGF family members. Human and mouse EGFs are very similar, but not identical in their physical and chemical properties. Of the 53 amino acid residues comprising each of the two polypeptides, 37 are common to both molecules, and three disulfide bonds are formed in the same relative positions.
애플리케이션
Epidermal Growth Factor from mouse has been used as a basal (N2B27) medium supplement for culturing differentiated mouse embryonic stem (E14) cells.
생화학적/생리학적 작용
EGF (epidermal growth factor) is involved in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Moreover, it was found to affect various biological activities like angiogenesis, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, modulation of the synthesis of a number of hormones, synthesis and turn-over of proteins of the extracellular matrix, calcium release from bone tissue (thus promoting bone resorption), chemoattraction of fibroblasts and epithelial cells, and alone or in combination with other cytokines, mediation of wound healing processes. EGF is mitogenic for a large variety cell types, including fibroblasts, epithelial cells, endothelial cells, chondrocytes, and SV40-3T3 cells.
물리적 형태
The product is lyophilized from a 0.2 μm-filtered solution of phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4.
문헌인용
1. Carpenter, G., and Cohen, S., Epidermal growth factor. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 48, 193-216 (1979).
2. Jorissen, R.N., et al., Epidermal growth factor: mechanisms of activation and signaling. Exp. Cell Res., 284, 31-53 (2003).
3. Herbst, R.S., Review of epidermal growth factor receptor biology. Int.J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol., Phys., 59, S21-S26 (2004).
4. Mehta, V.B., and Besner, G.E., HB-EGF promotes angiogenesis in endothelial cells via PI3-kinase and MAPK signaling pathways. Growth Factors, 25, 253-263 (2007).
5. Bower, J.M., et al., The inhibition of gastric acid secretion by epidermal growth factor. Experientia, 31, 825-826 (1975).
6. Schonbrunn, A., et.al., Epidermal growth factor and thyrotropin-releasing hormone act similarly on a clonal pituitary cell strain. Modulation of hormone production and inhibition of cell proliferation. J. Cell Biol., 85, 786-797 (1980).
7. Mimura, Y., et al., Epidermal growth factor induces fibronectin expression in human dermal fibroblasts via protein kinase C delta signaling pathway. J. Invest. Dermatol., 122, 1390-1398 (2004).
8. Warner, M.R. et al., Ametantrone inhibits prostaglandin-mediated resorption in bone organ culture. Prostaglandins, 28, 469-476 (1984).
9. Grotendorst, G.R., et al., EGF and TGF-alpha are potent chemoattractants for endothelial cells and EGF-like peptides are present at sites of tissue regeneration. J. Cell. Physiol., 139, 617623 (1989).
10. Schultz, G., et al., EGF and TGF-alpha in wound healing and repair. J. Cell. Biochem., 45, 346-352 (1991).
11. George-Nascimento, C., et al., Characterization of recombinant human epidermal growth factor produced in yeast. Biochemistry, 27, 797-802 (1988).
2. Jorissen, R.N., et al., Epidermal growth factor: mechanisms of activation and signaling. Exp. Cell Res., 284, 31-53 (2003).
3. Herbst, R.S., Review of epidermal growth factor receptor biology. Int.J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol., Phys., 59, S21-S26 (2004).
4. Mehta, V.B., and Besner, G.E., HB-EGF promotes angiogenesis in endothelial cells via PI3-kinase and MAPK signaling pathways. Growth Factors, 25, 253-263 (2007).
5. Bower, J.M., et al., The inhibition of gastric acid secretion by epidermal growth factor. Experientia, 31, 825-826 (1975).
6. Schonbrunn, A., et.al., Epidermal growth factor and thyrotropin-releasing hormone act similarly on a clonal pituitary cell strain. Modulation of hormone production and inhibition of cell proliferation. J. Cell Biol., 85, 786-797 (1980).
7. Mimura, Y., et al., Epidermal growth factor induces fibronectin expression in human dermal fibroblasts via protein kinase C delta signaling pathway. J. Invest. Dermatol., 122, 1390-1398 (2004).
8. Warner, M.R. et al., Ametantrone inhibits prostaglandin-mediated resorption in bone organ culture. Prostaglandins, 28, 469-476 (1984).
9. Grotendorst, G.R., et al., EGF and TGF-alpha are potent chemoattractants for endothelial cells and EGF-like peptides are present at sites of tissue regeneration. J. Cell. Physiol., 139, 617623 (1989).
10. Schultz, G., et al., EGF and TGF-alpha in wound healing and repair. J. Cell. Biochem., 45, 346-352 (1991).
11. George-Nascimento, C., et al., Characterization of recombinant human epidermal growth factor produced in yeast. Biochemistry, 27, 797-802 (1988).
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
시험 성적서(COA)
제품의 로트/배치 번호를 입력하여 시험 성적서(COA)을 검색하십시오. 로트 및 배치 번호는 제품 라벨에 있는 ‘로트’ 또는 ‘배치’라는 용어 뒤에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
이미 열람한 고객
Epidermal growth factor.
Carpenter G and Cohen S
Annual Review of Biochemistry, 48, 193-193 (1979)
Review of epidermal growth factor receptor biology.
Herbst RS
International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 59, S21-S21 (2004)
Epidermal growth factor and thyrotropin-releasing hormone act similarly on a clonal pituitary cell strain.
Schonbrunn A et al.
The Journal of Cell Biology, 85, 786-786 (1980)
EGF and TGF-alpha in wound healing and repair.
Schultz G et al.
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 45, 346-346 (1991)
Ametantrone inhibits prostaglandin-mediated resorption in bone organ culture.
Warner MR et al.
Prostaglandins, 28, 469-469 (1984)
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.