추천 제품
생물학적 소스
rat
Quality Level
항체 형태
purified antibody
항체 생산 유형
primary antibodies
클론
3H1, monoclonal
종 반응성
mouse
기술
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
western blot: suitable
동형
IgG
NCBI 수납 번호
UniProt 수납 번호
배송 상태
wet ice
타겟 번역 후 변형
unmodified
유전자 정보
mouse ... Mlkl(74568)
일반 설명
MLKL, also known as Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein, and encoded by the gene MLKL, is an interesting protein that is required for the execution of programmed necrosis or necroptosis, for example in response to TNF-alpha induced necrosis. MLKL is a component of the "necrosome," the multiprotein complex that triggers tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced cell death by necroptosis. The programmed necrosis induced by TNF-α also requires the activities of the receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinases RIP1 and RIP3 and they too interact directly with the mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein MLKL. RIP3 is an essential upstream kinase in necroptosis. The pseudokinase MLKL functions as a substrate of RIP3 to mediate downstream signaling and when complexed to MLKL the RIP3-MLKL complex is stabilized by AMP-PNP to adopt an inactive conformation.
면역원
Epitope: Brace region.
KLH-conjugated linear peptide corresponding to a sequence from the two-helix linker (Brace) region N-terminal to the pseudokinase domain of mouse MLKL (Hildebrand, J.M., et al. (2014). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111(42):15072-15077; Murphy, J.M., et al. (2013). Immunity. 39(3):443-453).
애플리케이션
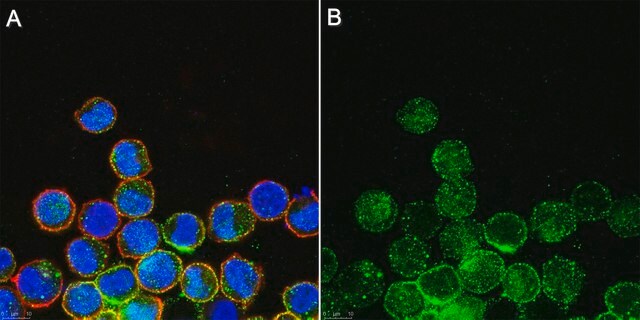
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected MLKL in mouse dermal fibroblasts (MDFs) from wild-type, but not Mlkl-/- mice (Courtesy of Prof. James M. Murphy, Walter and Eliza Hall Institute, Australia).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot immunoprecipitated MLKL from soluble extract of Mlkl-/- mouse dermal fibroblasts (MDFs) harboring doxycycline-inducible wild-type mouse MLKL expression construct only after, but not before doxycycline treatment (Murphy, J.M., et al. (2013). Immunity. 39(3):443-453).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected Q-VD-OPh (TSQ; Cat. No. 551476) treatment-induced membrane translocation of murine and equine MLKL N-terminal fragment (a.a. 1-180 and 1-189, respectively) exogenously expressed in mouse dermal fibroblasts (MDFs) from Mlkl-/- mice (Tanzer, M.C., et al. (2016). Cell Death Differ.. In press).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected MLKL in human HT-29 and U937 cells (Tanzer, M.C., et al. (2015). Biochem. J. 471(2):255-265).
Western Blotting Analysis: Representative lots detected MLKL membrane translocation in mouse dermal fibroblasts (MDFs) upon Q-VD-OPh (TSQ; Cat. No. 551476) treatment (Tanzer, M.C., et al. (2015). Biochem. J. 471(2):255-265; Hildebrand, J.M., et al. (2014). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111(42):15072-15077).
Western Blotting Analysis: Representative lots detected MLKL expression in L292 mouse fibroblasts, as well as in mouse dermal fibroblasts (MDFs), mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDMs) from wild-type, but not Mlkl-/- mice (Cook, W.D., et al. (2014). Cell Death Differ. 21(10):1600-1612; Murphy, J.M., et al. (2013). Immunity. 39(3):443-453).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected recombinant full-length mouse MLKL as well as a.a. 1-180 and a.a. 124-464, but not a.a. 1-125 or a.a. 179-464, MLKL fragments (Hildebrand, J.M., et al. (2014). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111(42):15072-15077).
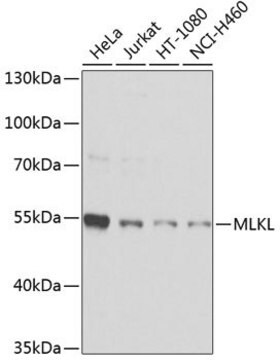
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected MLKL expression in all tissues tested except brain from wild-type mice, while no target band was seen in any tissues from Mlkl-/- mice (Murphy, J.M., et al. (2013). Immunity. 39(3):443-453).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot immunoprecipitated MLKL from soluble extract of Mlkl-/- mouse dermal fibroblasts (MDFs) harboring doxycycline-inducible wild-type mouse MLKL expression construct only after, but not before doxycycline treatment (Murphy, J.M., et al. (2013). Immunity. 39(3):443-453).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected Q-VD-OPh (TSQ; Cat. No. 551476) treatment-induced membrane translocation of murine and equine MLKL N-terminal fragment (a.a. 1-180 and 1-189, respectively) exogenously expressed in mouse dermal fibroblasts (MDFs) from Mlkl-/- mice (Tanzer, M.C., et al. (2016). Cell Death Differ.. In press).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected MLKL in human HT-29 and U937 cells (Tanzer, M.C., et al. (2015). Biochem. J. 471(2):255-265).
Western Blotting Analysis: Representative lots detected MLKL membrane translocation in mouse dermal fibroblasts (MDFs) upon Q-VD-OPh (TSQ; Cat. No. 551476) treatment (Tanzer, M.C., et al. (2015). Biochem. J. 471(2):255-265; Hildebrand, J.M., et al. (2014). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111(42):15072-15077).
Western Blotting Analysis: Representative lots detected MLKL expression in L292 mouse fibroblasts, as well as in mouse dermal fibroblasts (MDFs), mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDMs) from wild-type, but not Mlkl-/- mice (Cook, W.D., et al. (2014). Cell Death Differ. 21(10):1600-1612; Murphy, J.M., et al. (2013). Immunity. 39(3):443-453).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected recombinant full-length mouse MLKL as well as a.a. 1-180 and a.a. 124-464, but not a.a. 1-125 or a.a. 179-464, MLKL fragments (Hildebrand, J.M., et al. (2014). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111(42):15072-15077).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected MLKL expression in all tissues tested except brain from wild-type mice, while no target band was seen in any tissues from Mlkl-/- mice (Murphy, J.M., et al. (2013). Immunity. 39(3):443-453).
This Anti-MLKL Antibody, clone 3H1 is validated for use in Immunocytochemistry, Immunoprecipitation, and Western Blotting for the detection of MLKL.
품질
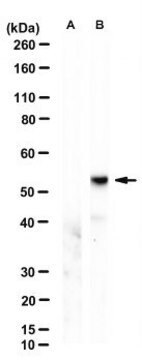
Evaluated by Western Blotting in mouse heart tissue lysate.
Western Blotting Analysis: 0.5 µg/mL of this antibody detected MLKL in 10 µg of mouse heart tissue lysate.
Western Blotting Analysis: 0.5 µg/mL of this antibody detected MLKL in 10 µg of mouse heart tissue lysate.
표적 설명
~52 kDa observed. 54.48/30.28 (human isoform 1/2) and 54.32/53.38 kDa (mouse isoform 1/2) calculated. Uncharacterized band(s) may be observed in some cell lysates.
물리적 형태
Format: Purified
Purified rat IgG in buffer containing 0.1 M Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl with 0.05% sodium azide.
기타 정보
Concentration: Please refer to the Certificate of Analysis for the lot-specific concentration.
적합한 제품을 찾을 수 없으신가요?
당사의 제품 선택기 도구.을(를) 시도해 보세요.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
시험 성적서(COA)
제품의 로트/배치 번호를 입력하여 시험 성적서(COA)을 검색하십시오. 로트 및 배치 번호는 제품 라벨에 있는 ‘로트’ 또는 ‘배치’라는 용어 뒤에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
The pseudokinase MLKL mediates necroptosis via a molecular switch mechanism.
Murphy, James M, et al.
Immunity, 39, 443-453 (2013)
RIPK1- and RIPK3-induced cell death mode is determined by target availability.
Cook, WD; Moujalled, DM; Ralph, TJ; Lock, P; Young, SN; Murphy, JM; Vaux, DL
Cell Death and Differentiation null
Snahel Patel et al.
Cell death and differentiation, 27(1), 161-175 (2019-05-19)
The kinase RIP1 acts in multiple signaling pathways to regulate inflammatory responses and it can trigger both apoptosis and necroptosis. Its kinase activity has been implicated in a range of inflammatory, neurodegenerative, and oncogenic diseases. Here, we explore the effect
Joseph Sarhan et al.
Cell death and differentiation, 26(2), 332-347 (2018-05-23)
Interferons (IFNs) are critical determinants in immune-competence and autoimmunity, and are endogenously regulated by a low-level constitutive feedback loop. However, little is known about the functions and origins of constitutive IFN. Recently, lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced IFN was implicated as a driver
Hayley I Muendlein et al.
Cell reports, 30(3), 699-713 (2020-01-23)
Receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) and 3 (RIPK3) are well known for their capacity to drive necroptosis via mixed-lineage kinase-like domain (MLKL). Recently, RIPK1/3 kinase activity has been shown to drive inflammation via activation of MAPK signaling. However, the regulatory
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.