추천 제품
생물학적 소스
mouse
Quality Level
항체 형태
ascites fluid
항체 생산 유형
primary antibodies
클론
3C4, monoclonal
종 반응성
human
제조업체/상표
Chemicon®
기술
electron microscopy: suitable
flow cytometry: suitable
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable (paraffin)
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
동형
IgG1κ
NCBI 수납 번호
UniProt 수납 번호
배송 상태
dry ice
타겟 번역 후 변형
unmodified
유전자 정보
human ... COL6A3(1293)
일반 설명
Collagen alpha-3(VI) chain (UniProt P12111; also known as Collagen VI alpha-3 polypeptide) is encoded by the COL6A3 gene (Gene ID 1293) in human. Type VI collagen is an extracellular matrix (ECM) component present in virtually all connective tissues, including cartilage, bone, tendon, muscles and cornea, where it forms microfibrils in close association with basement membranes. In addition to anchoring the basement membrane to the pericellular matrix in muscle, research also indicates a role for collagen VI in cell signaling and cell migration. The basic structural unit of collagen VI is a heterotrimer composed of the alpha-1(VI), alpha-2(VI), and alpha-3(VI) chains (encoded by the COL6A1, COL6A2, and COL6A3 genes, respectively). The α1(VI) and α2(VI) chains are similar in size and domain structure, they contain a 335- or 336-amino acid triple helix region that is characteristic of all collagens. Flanking the triple helix are domains homologous to the A-type domains found in von Willebrand factor (VWA domains). α1(VI) and α2(VI) contain one VWA domain N-terminal to the triple helix (N1) and two VWA domains C-terminal of the helix (C1 and C2). The α3(VI) chain, on the other hand, is much larger with 10 N-terminal (N1–N10) and two C-terminal VWA domains (C1 and C2), and several other types of identifiable domains in the C terminal region (C3–C5). Mutations in the COL6A1, COL6A2, and COL6A3 genes are known causes of Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) and Bethlem myopathy (BM). Three additional type VI collagen chains have been reported in 2008 (α4(VI), α5(VI) and α6(VI) chains encoded by COL6A4, COL6A5, and COL6A6, respectively).
특이성
Clone 3C4 targets the non-helical region of alpha-3(VI) chain.
Other species not tested.
면역원
Epitope: Non-helical region.
Purified human collagen VI
애플리케이션
Flow Cytometry Analysis: A representative lot detected intracellular type VI collagen retention by flow cytometry using permeabilized and non-permeabilized fibroblasts isolated from both healthy individuals, as well as Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) and Bethlem myopathy (BM) patients (Kim, J., et al. (2012). Neuromuscul. Disord. 22(2):139-148).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: Representative lots detected extracellular type VI collagen immunoreactivity in cultured fibroblasts isolated from Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) and Bethlem myopathy (BM) patients by fluorescent immunocytochemistry (Kim, J., et al. (2012). Neuromuscul. Disord. 22(2):139-148; Allamand, V., et al. (2011). Skelet Muscle. 1:30; Briñas, L., et al. (2010). Ann. Neurol. 68(4):511-520; Jimenez-Mallebrera, C., et al. (2006). Neuromuscul. Disord. 16(9-10):571-582; Tétreault, M., et al. (2004). Brain. 129(Pt 8):2077-2084; Zhang, R.Z., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(46):43557-43564).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected exogenously expressed wild-type α3(VI) chain, as well as α3(VI) chain with G49A or G301V mutation in SaOS-2 transfectants by fluorescent immunocytochemistry (Lamandé, S.R., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(3):1949-1956).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: Representative lots immunostained extracellular type VI collagen fibrils in human MG63 osteosarcoma cells and primary foreskin fibroblasts cultures (Bruns, R.R., et al. (1986). J. Cell Biol. 103(2):393-404; Engvall, E., et al. (1986). J. Cell Biol. 102(3):703-710).
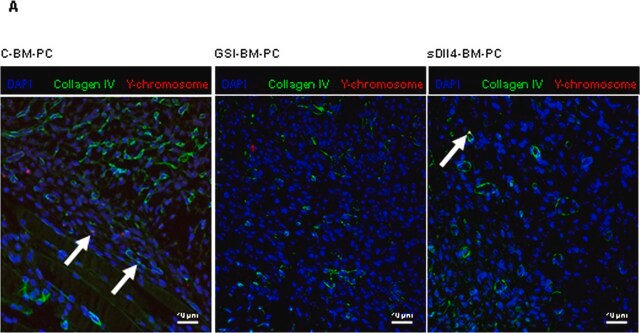
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected human type VI collagen immunoreactivity in frozen muscle tissue sections from mice grafted with human synovial stem cells (hSSCs) by fluorescent immunohistochemistry (Meng, J., et al. (2010). Neuromuscul. Disord. 20(1):6-15).
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: Representative lots detected type VI collagen immunoreactivity in muscle and skin samples from congenital muscular dystrophy (CMD) and Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) patients by fluorescent immunohistochemistry using frozen tissue sections (Peat, R.A., et al. (2008). Neurology. 71(5):312-321; Jimenez-Mallebrera, C., et al. (2006). Neuromuscul. Disord. 16(9-10):571-582).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot co-immunoprecipitated type VI collagen α1(VI) and α2(VI) chains with wild-type α3(VI) chain, as well as α3(VI) chain with G16S or G49A mutation. Impaired α1(VI) and α2(VI) co-IP was observed with α3(VI) G301V mutant (Lamandé, S.R., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(3):1949-1956).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot immunoprecipitated type VI collagen alpha chains from Triton X-100 extracts of MRC-5 human lung fibroblasts (Engvall, E., et al. (1986). J. Cell Biol. 102(3):703-710).
Electron Microscopy Analysis: A representative lot detected reduced extracellular type VI collagen immunoreactivity in cultured fibroblasts isolated from an Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) patient (Zhang, R.Z., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(46):43557-43564).
Electron Microscopy Analysis: A representative lot immunostained extracellular filaments and fibrils by binding to the band (non-helical) region of the type VI collagen fibrils using cultured human foreskin fibroblasts (Bruns, R.R., et al. (1986). J. Cell Biol. 103(2):393-404).
Dot Blot Analysis: A representative lot detected exogenously expressed wild-type α3(VI) chain, as well as α3(VI) chain with G49A or G301V mutation in the medium of cultured SaOS-2 transfectants (Lamandé, S.R., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(3):1949-1956).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: Representative lots detected extracellular type VI collagen immunoreactivity in cultured fibroblasts isolated from Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) and Bethlem myopathy (BM) patients by fluorescent immunocytochemistry (Kim, J., et al. (2012). Neuromuscul. Disord. 22(2):139-148; Allamand, V., et al. (2011). Skelet Muscle. 1:30; Briñas, L., et al. (2010). Ann. Neurol. 68(4):511-520; Jimenez-Mallebrera, C., et al. (2006). Neuromuscul. Disord. 16(9-10):571-582; Tétreault, M., et al. (2004). Brain. 129(Pt 8):2077-2084; Zhang, R.Z., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(46):43557-43564).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected exogenously expressed wild-type α3(VI) chain, as well as α3(VI) chain with G49A or G301V mutation in SaOS-2 transfectants by fluorescent immunocytochemistry (Lamandé, S.R., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(3):1949-1956).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: Representative lots immunostained extracellular type VI collagen fibrils in human MG63 osteosarcoma cells and primary foreskin fibroblasts cultures (Bruns, R.R., et al. (1986). J. Cell Biol. 103(2):393-404; Engvall, E., et al. (1986). J. Cell Biol. 102(3):703-710).
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected human type VI collagen immunoreactivity in frozen muscle tissue sections from mice grafted with human synovial stem cells (hSSCs) by fluorescent immunohistochemistry (Meng, J., et al. (2010). Neuromuscul. Disord. 20(1):6-15).
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: Representative lots detected type VI collagen immunoreactivity in muscle and skin samples from congenital muscular dystrophy (CMD) and Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) patients by fluorescent immunohistochemistry using frozen tissue sections (Peat, R.A., et al. (2008). Neurology. 71(5):312-321; Jimenez-Mallebrera, C., et al. (2006). Neuromuscul. Disord. 16(9-10):571-582).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot co-immunoprecipitated type VI collagen α1(VI) and α2(VI) chains with wild-type α3(VI) chain, as well as α3(VI) chain with G16S or G49A mutation. Impaired α1(VI) and α2(VI) co-IP was observed with α3(VI) G301V mutant (Lamandé, S.R., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(3):1949-1956).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot immunoprecipitated type VI collagen alpha chains from Triton X-100 extracts of MRC-5 human lung fibroblasts (Engvall, E., et al. (1986). J. Cell Biol. 102(3):703-710).
Electron Microscopy Analysis: A representative lot detected reduced extracellular type VI collagen immunoreactivity in cultured fibroblasts isolated from an Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) patient (Zhang, R.Z., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(46):43557-43564).
Electron Microscopy Analysis: A representative lot immunostained extracellular filaments and fibrils by binding to the band (non-helical) region of the type VI collagen fibrils using cultured human foreskin fibroblasts (Bruns, R.R., et al. (1986). J. Cell Biol. 103(2):393-404).
Dot Blot Analysis: A representative lot detected exogenously expressed wild-type α3(VI) chain, as well as α3(VI) chain with G49A or G301V mutation in the medium of cultured SaOS-2 transfectants (Lamandé, S.R., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(3):1949-1956).
Research Category
Cell Structure
Cell Structure
Research Sub Category
ECM Proteins
ECM Proteins
This Anti-Collagen Type VI Antibody, clone 3C4 is validated for use in Dot Blot, Electron Microscopy, Flow Cytometry, Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), and Immunoprecipitation for the detection of collagen VI alpha-3 chain.
표적 설명
343.7/321.4/113.2/278.2/134.7 kDa (isoform 1/2/3/4/5 pro-form) and 340.8/318.5/110.4/275.3/131.8 kDa (isoform 1/2/3/4/5 mature form) calculated
물리적 형태
Liquid
Unpurified.
저장 및 안정성
Maintain frozen at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
법적 정보
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
면책조항
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
적합한 제품을 찾을 수 없으신가요?
당사의 제품 선택기 도구.을(를) 시도해 보세요.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
시험 성적서(COA)
제품의 로트/배치 번호를 입력하여 시험 성적서(COA)을 검색하십시오. 로트 및 배치 번호는 제품 라벨에 있는 ‘로트’ 또는 ‘배치’라는 용어 뒤에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
ColVI myopathies: where do we stand, where do we go?
Allamand, V; Bri?as, L; Richard, P; Stojkovic, T; Quijano-Roy, S; Bonne, G
Skeletal Muscle null
C Jimenez-Mallebrera et al.
Neuromuscular disorders : NMD, 16(9-10), 571-582 (2006-08-29)
Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) is caused by recessive and dominant mutations in COL6A genes. We have analysed collagen VI expression in 14 UCMD patients. Sequencing of COL6A genes had identified homozygous and heterozygous mutations in 12 cases. Analysis of
Kinked collagen VI tetramers and reduced microfibril formation as a result of Bethlem myopathy and introduced triple helical glycine mutations.
Lamande, Shireen R, et al.
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 1949-1956 (2002)
Type VI collagen in extracellular, 100-nm periodic filaments and fibrils: identification by immunoelectron microscopy.
Bruns, R R, et al.
The Journal of cell biology, 103, 393-404 (1986)
Laura Briñas et al.
Annals of neurology, 68(4), 511-520 (2010-10-27)
Mutations in the genes encoding the extracellular matrix protein collagen VI (ColVI) cause a spectrum of disorders with variable inheritance including Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy, Bethlem myopathy, and intermediate phenotypes. We extensively characterized, at the clinical, cellular, and molecular levels
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.