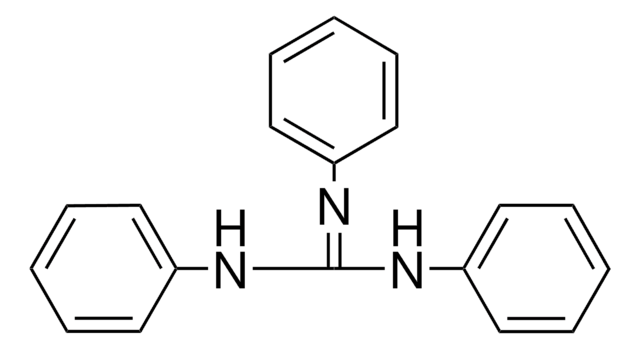
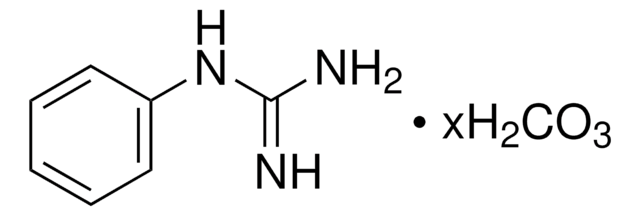
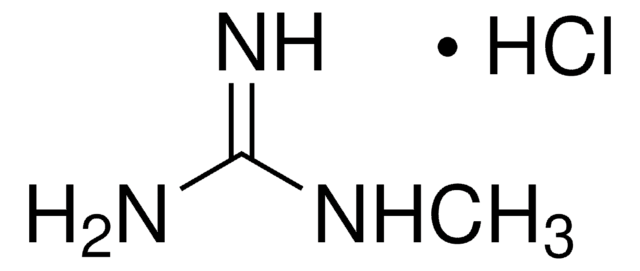
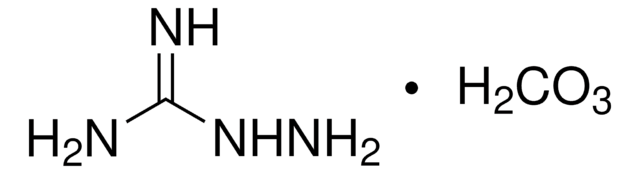추천 제품
Quality Level
분석
95%
mp
242-244 °C (dec.) (lit.)
SMILES string
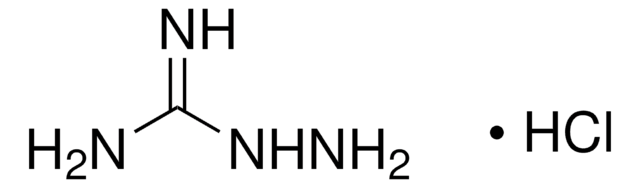
NC(=N)Nc1nc2ccccc2[nH]1
InChI
1S/C8H9N5/c9-7(10)13-8-11-5-3-1-2-4-6(5)12-8/h1-4H,(H5,9,10,11,12,13)
InChI key
JJWCTKUQWXYIIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
개인 보호 장비
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
M Fronius et al.
The Journal of membrane biology, 195(1), 43-51 (2003-09-23)
In the present study we investigated the effect of extracellular gadolinium on amiloride-sensitive Na(+) current across Xenopus alveolar epithelium by Ussing chamber experiments and studied its direct effect on epithelial Na(+) channels with the patch-clamp method. As observed in various
A Pinelli et al.
Arzneimittel-Forschung, 34(8), 890-894 (1984-01-01)
In this study 2-guanidinebenzimidazole (GBI) and 1-phenylbiguanide (PBG) appear to be capable of decreasing gastric acid secretion, while the compounds dimethylbiguanide and cyanoguanidine do not. Thus, the antisecretory effect is present when the biguanide groups are associated with lipophilic molecules.
K Eskesen et al.
Acta physiologica Scandinavica, 136(4), 547-550 (1989-08-01)
Serosal amiloride inhibits Na+, K+ and Cl- efflux and reduces short-circuit current and transepithelial conductance in noradrenaline-stimulated frog skin in which the sodium channels in the apical membrane are blocked by amiloride. BIG (benzimidazoleguanidine) inhibits Na+ and K+ efflux and
Voltage-gated proton channels from fungi highlight role of peripheral regions in channel activation.
Chang Zhao et al.
Communications biology, 4(1), 261-261 (2021-02-28)
Here, we report the identification and characterization of the first proton channels from fungi. The fungal proteins are related to animal voltage-gated Hv channels and are conserved in both higher and lower fungi. Channels from Basidiomycota and Ascomycota appear to
P Komwatana et al.
The Journal of membrane biology, 162(3), 225-232 (1998-05-16)
We have previously shown that epithelial Na+ channels in mouse mandibular gland duct cells are controlled by cytosolic Na+ and Cl-, acting, respectively, via Go and Gi proteins. Since we found no evidence for control of epithelial Na+ channels by
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.