추천 제품
설명
0.2 μm sterile filtered
suitable for 3D bioprinting applications
Quality Level
형태
gel form (viscous)
불순물
≤5 CFU/g Bioburden (Fungal)
≤5 CFU/g Bioburden (Total Aerobic)
색상
white
pH
6.5-7.5
응용 분야
3D bioprinting
저장 온도
2-8°C
유사한 제품을 찾으십니까? 방문 제품 비교 안내
관련 카테고리
애플리케이션
TissueFab®- GelMA-Bone-UV bioink is designed for promoting osteogenic differentiation of stem cells. It is based on Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) - Hydroxyapatite (HAp) hydrogel system. HAp is a highly crystalline form of calcium phosphate. HAp has a chemical similarity with the mineralized phase of bone which accounts for their excellent biocompatibility and osteoinductive and osteoconductive properties favorable for bone regeneration. HAp-containing hydrogels has been studied in literature to demonstrate their processability with different additive manufacturing approaches. Printing of cell laden structures with HAp containing bioink formulations have shown superior osteogenic properties.
법적 정보
TISSUEFAB is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
시험 성적서(COA)
제품의 로트/배치 번호를 입력하여 시험 성적서(COA)을 검색하십시오. 로트 및 배치 번호는 제품 라벨에 있는 ‘로트’ 또는 ‘배치’라는 용어 뒤에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
Tunable hydrogel composite with two-step processing in combination with innovative hardware upgrade for cell-based threedimensional bioprinting
Wust S, et al.
Acta Biomaterialia, 10, 630?40-630?40 (2014)
Tunable hydrogel composite with two-step processing in combination with innovative hardware upgrade for cell-based threedimensional bioprinting.
Wust S. et al.
Acta Biomaterialia, 10, 630-640 (2014)
Nano hydroxyapatite particles promote osteogenesis in a three-dimensional bio-printing construct consisting of alginate/gelatin/hASCs
Wang X F et al.
Royal Society of Chemistry Advances, 6, 6832-6842 (2016)
Mehdi Sadat-Shojai et al.
Materials science & engineering. C, Materials for biological applications, 49, 835-843 (2015-02-18)
The ability to encapsulate cells in three-dimensional (3D) protein-based hydrogels is potentially of benefit for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. However, as a result of their poor mechanical strength, protein-based hydrogels have traditionally been considered for soft tissue engineering only.
Yicong Zuo et al.
ACS applied materials & interfaces, 7(19), 10386-10394 (2015-05-01)
Modular tissue engineering holds great potential in regenerating natural complex tissues by engineering three-dimensional modular scaffolds with predefined geometry and biological characters. In modular tissue-like construction, a scaffold with an appropriate mechanical rigidity for assembling fabrication and high biocompatibility for
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.


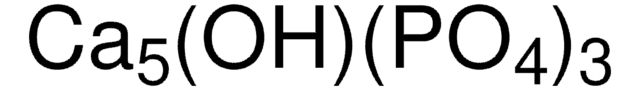
![Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid] natural origin](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/129/476/7d1c924b-f644-4889-a2d6-d7a923ce382c/640/7d1c924b-f644-4889-a2d6-d7a923ce382c.png)

