추천 제품
형태
solid
구성
Dye content, 90%
mp
203 °C (dec.) (lit.)
solubility
95% ethanol: 0.1%
λmax
545 nm
ε (흡광계수)
≥11000 at 235-241 nm in ethanol: water (1:1) at 0.004%
≥16000 at 286-292 nm in ethanol: water (1:1) at 0.004%
≥78000 at 543-549 nm in ethanol: water (1:1) at 0.004%
응용 분야
diagnostic assay manufacturing
hematology
histology
저장 온도
room temp
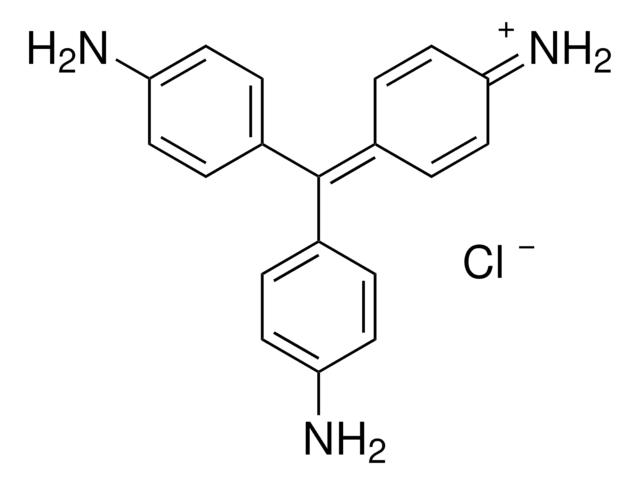
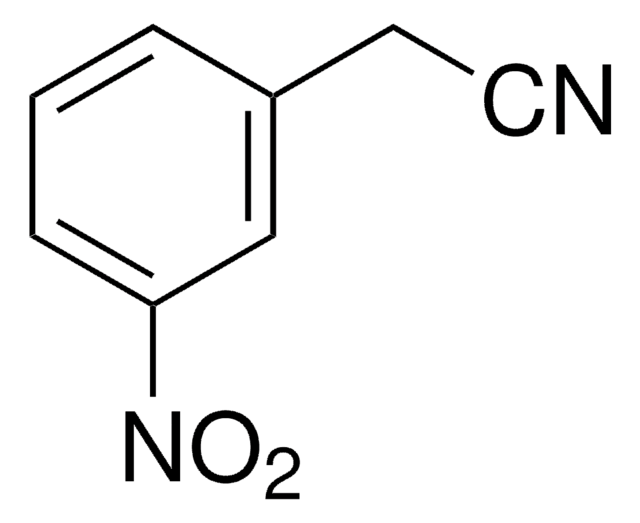
SMILES string
CC(O)=O.Nc1ccc(cc1)C(\c2ccc(N)cc2)=C3\C=CC(=N)C=C3
InChI
1S/C19H17N3.C2H4O2/c20-16-7-1-13(2-8-16)19(14-3-9-17(21)10-4-14)15-5-11-18(22)12-6-15;1-2(3)4/h1-12,20H,21-22H2;1H3,(H,3,4)
InChI key
YIXIVOYGLPFDCY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
유사한 제품을 찾으십니까? 방문 제품 비교 안내
생화학적/생리학적 작용
Pararosaniline acetate is one of the components of basic fuchsin. It acts as a reversible, linear inhibitor of horse butyrylcholinesterase (BChE).
기타 정보
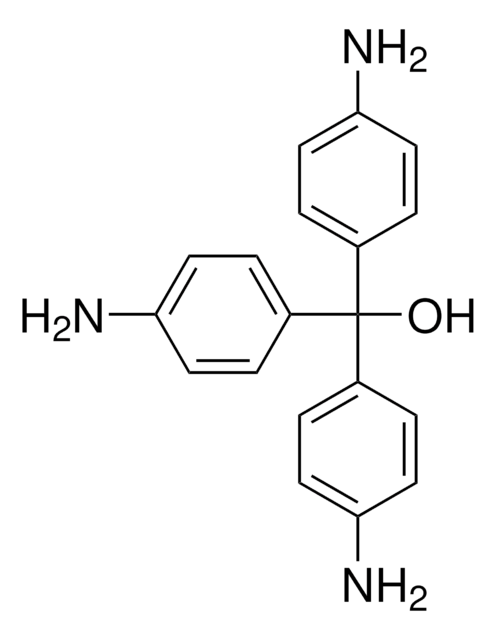
This is the pure, principal component of mixtures commonly referred to as Basic Fuchsin.
법적 정보
Magenta is a trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
신호어
Warning
유해 및 위험 성명서
Hazard Classifications
Carc. 2
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
개인 보호 장비
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Comparative effects of cationic triarylmethane, phenoxazine and phenothiazine dyes on horse serum butyrylcholinesterase.
Yucel YY
Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 478, 201-205 (2008)
Michael D. Larra?aga, Richard J. Lewis, Robert A. Lewis
Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary (2016)
Tuba Küçükkilinç et al.
Archives of biochemistry and biophysics, 440(2), 118-122 (2005-07-23)
The inhibitory effects of the cationic triarylmethane (TAM+) dyes, pararosaniline (PR+), malachite green (MG+), and methyl green (MeG+) on human plasma cholinesterase (BChE) were studied at 25 degrees C in 100 mM Mops, pH 8.0, with butyrylthiocholine as substrate. PR+
Jingli Xie et al.
Chemical communications (Cambridge, England), (5)(5), 576-578 (2008-01-23)
Salts of the pararosaniline dye cation and four polyoxometalate cluster anions have been isolated under both ambient and hydrothermal conditions; structural and initial spectroscopic data are consistent with significant perturbation of ion electronic states induced by charge-assisted N-H---O hydrogen bonds.
Fernando Maldonado et al.
Journal of colloid and interface science, 351(2), 466-471 (2010-08-28)
Adsolubilisation has been defined as the incorporation to solid-water interfaces of molecules that do not adsorb spontaneously to such interfaces, but can be incorporated through an interaction with an adsorbing surfactant molecule. The aim of this work was to study
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.