162957
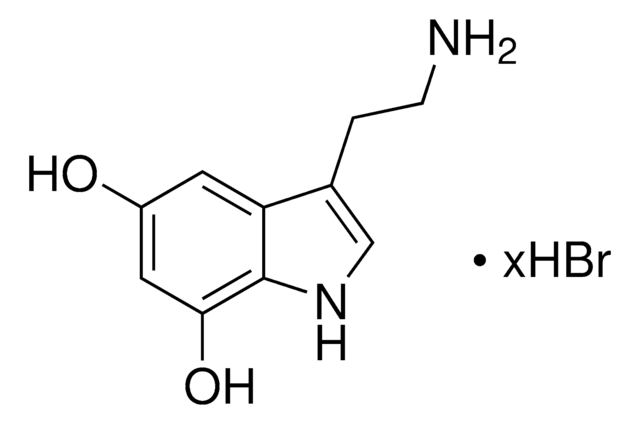
6-Hydroxydopamine hydrobromide
95% (HPLC), powder, neurotoxin
동의어(들):
2,4,5-Trihydroxyphenethylamine hydrobromide, 2,5-Dihydroxytyramine hydrobromide, 2-(2,4,5-Trihydroxyphenyl)ethylamine hydrobromide, 6-OHDA
로그인조직 및 계약 가격 보기
모든 사진(3)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
(HO)3C6H2CH2CH2NH2 · HBr
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
250.09
Beilstein:
3713280
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC 코드:
12352116
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.77
추천 제품
제품명
6-Hydroxydopamine hydrobromide, 95%
분석
95%
양식
powder
mp
216-220 °C (lit.)
저장 온도
−20°C
SMILES string
Br.NCCc1cc(O)c(O)cc1O
InChI
1S/C8H11NO3.BrH/c9-2-1-5-3-7(11)8(12)4-6(5)10;/h3-4,10-12H,1-2,9H2;1H
InChI key
MLACDGUOKDOLGC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
유사한 제품을 찾으십니까? 방문 제품 비교 안내
일반 설명
Solutions should be freshly prepared and protected from exposure to light.
애플리케이션
6-Hydroxydopamine hydrobromide has been used:
- to induce Parkinson′s disease (PD) in mouse models to study the effects of tubastatin A (TBA) on nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain and leucine-rich repeat pyrin 3 domain (NLRP3) activation and cell injury in SH-SY5Y cells
- to induce pharmacological ablation of the sympathetic nerves to study the effect of hepatic sympathetic nerve activity (SNA) on hepatic steatosis during diet-induced obesity in mice
- to induce oxidative stress in mesencephalic cells to study its effect on p75NTR signaling in neuronal cells of the ventral mesencephalon
생화학적/생리학적 작용
6-Hydroxydopamine hydrobromide (6-OHDA) is a neurotoxin that elicits oxidative damage and destroys catecholaminergic or sympathetic terminals. It is commonly used to induce Parkinson′s disease in the experimental model. 6-OHDA exerts cytotoxicity by generating reactive oxygen species, initiating cellular stress and cell death.
신호어
Warning
유해 및 위험 성명서
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
표적 기관
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
개인 보호 장비
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Woori Kim et al.
Neurobiology of aging, 35(7), 1712-1721 (2014-02-25)
Dopamine (DA) neurons in sporadic Parkinson's disease (PD) display dysregulated gene expression networks and signaling pathways that are implicated in PD pathogenesis. Micro (mi)RNAs are regulators of gene expression, which could be involved in neurodegenerative diseases. We determined the miRNA
Yun-Qi Xu et al.
CNS neuroscience & therapeutics, 19(3), 170-177 (2013-01-03)
In addition to their original applications for lowering cholesterol, statins display multiple neuroprotective effects. Inflammatory reactions and the PI3K/AKT/caspase 3 pathway are strongly implicated in dopaminergic neuronal death in Parkinson's disease (PD). This study aims to investigate how simvastatin affects
Julio C Tobón-Velasco et al.
Toxicology, 304, 109-119 (2013-01-01)
6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) is a neurotoxin that generates an experimental model of Parkinson's disease in rodents and is commonly employed to induce a lesion in dopaminergic pathways. The characterization of those molecular mechanisms linked to 6-OHDA-induced early toxicity is needed to
C C Real et al.
Neuroscience, 237, 118-129 (2013-02-12)
Physical exercise is known to produce beneficial effects to the nervous system. In most cases, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is involved in such effects. However, little is known on the role of BDNF in exercise-related effects on Parkinson's disease (PD).
Ilse S Pienaar et al.
Experimental neurology, 248, 213-223 (2013-06-19)
The pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN) controls various physiological functions, whilst being deemed a suitable target for low-frequency stimulation therapy for alleviating aspects of Parkinson's disease (PD). Previous studies showed that the PPN contains mainly cholinergic, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic and glutamatergic neurons.
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.