Purification or Removal of Albumin and IgG
Albumin & IgG Depletion Sepharose High Performance
Albumin and IgG are the most abundant proteins in plasma which tend to obscure the signals of less abundant proteins, preventing accurate detection. The high abundance of albumin and IgG also interferes with the detection of other proteins by preventing a sufficient amount of less abundant proteins from being included in the analysis. By depleting samples of albumin and IgG, the quality and depth of the analysis can be greatly enhanced. Depletion of the two removes more than 60% of the total protein content in human plasma, allowing proteins normally obscured by albumin and IgG to be visualized.
Albumin & IgG Depletion Sepharose High Performance is available prepacked in in HiTrap® and SpinTrap™ formats for removal of human serum albumin (HSA) and IgG. Both column types are prepacked with a mixture of antiHSA Sepharose High Performance and Protein G Sepharose High Performance. The ligand of antiHSA Sepharose High Performance is based on a single domain antibody fragment with high specificity and capacity for HSA. The ligand of Protein G Sepharose High Performance is derived from the IgG binding regions of Protein G, a cell surface protein of Streptococcus bacteria. The protein G ligand binds human IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4.
The primary use of the products is small-scale preparation of protein samples prior to downstream analyses such as 1-D or 2-D gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry (MS).The primary use of the products is small-scale preparation of protein samples prior to downstream analyses such as 1-D or 2-D gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry (MS).
A lower sample volume should be used when applying plasma containing albumin and IgG above the normal levels of human plasma (40 mg albumin/mL and 15 mg IgG/mL).
Chromatography Medium Characteristics
Table 3.3 shows the characteristics of the chromatography medium.
1 Short term refers to the pH interval for regeneration, cleaning-in-place, and sanitization procedures. Long term refers to the pH interval over which the medium is stable over a long period of time without adverse effects on its subsequent chromatographic performance.
Purification Options
The purification options for HiTrap® Albumin & IgG Depletion and Albumin & IgG Depletion SpinTrap™ column are shown in
Table 3.4.
1Human plasma containing ~ 40 mg albumin/mL and ~ 15 mg IgG/mL. Results according to ELISA: > 95% albumin depletion and > 90% IgG depletion.
Purification examples
HiTrap® Albumin & IgG Depletion can be used for depletion of human plasma without dilution of the sample before loading. A volume of 150 µL human plasma was applied to the 1 mL column, and the unbound fraction containing the depleted sample was collected. The depletion of albumin and IgG is shown by SDS-PAGE analysis (Figure 3.4). The depletion level was also determined by ELISA, and the result for the unbound fraction was 99% albumin depletion and 98% IgG depletion.
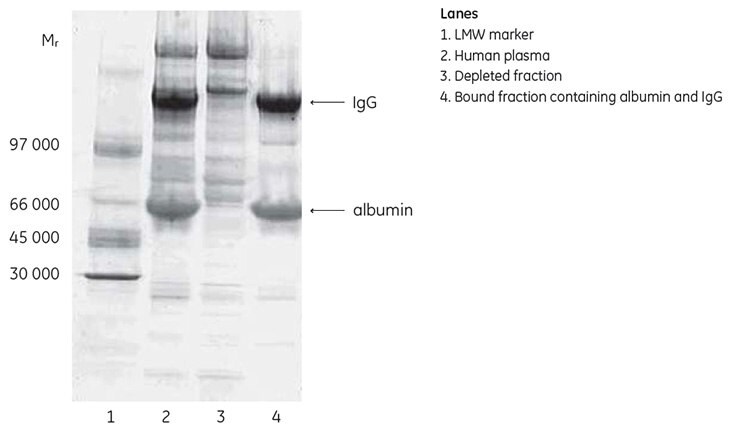
Figure 3.4.Deep Purple stained SDS-PAGE analysis (nonreducing conditions) of fractions from the depletion of human plasma using HiTrap® Albumin & IgG Depletion.
Performing a Separation
Binding buffer: 20 mM sodium phosphate, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4.
Elution buffer: 100 mM glycine-HCl, pH 2.7
Sample preparation: Dilution of the human plasma is not required. Filter the human plasma through a 0.22 or 0.45 µm filter shortly before applying it to the column.
HiTrap® Albumin and IgG Depletion
A flow rate of 1 mL/min is recommended for the entire depletion procedure.
- Fill the pump tubing with binding buffer. Remove the stopper and the snap-off end from the column and connect it to the pump tubing ‘drop-to-drop’ to avoid introducing air into the system.
- Wash the column with 5 mL binding buffer to remove the 20% ethanol storage solution.
- Equilibrate with 10 mL of binding buffer.
- Apply 150 µL filtrated human plasma and wash with at least 5 mL binding buffer until the absorbance reaches a steady baseline. Collect the sample flowthrough during sample application and wash. The flowthrough contains the depleted sample.
- Optional: Elute and collect the bound proteins (albumin and IgG) with 10 mL of elution buffer.
Note: Step 5 should be performed if the column is to be reused or if the bound albumin and IgG fraction is to be analyzed.
For the manual depletion procedure (without using a pump), the syringe is connected to the column by the provided Luer connector. Be sure to use a flow rate of approximately 1 mL/min.
Note that too high a flow rate will damage the packing of the chromatography medium and result in high back pressure.
Albumin & IgG Depletion SpinTrap™
- Remove storage solution
- A. Invert and shake the SpinTrap™ column repeatedly to resuspend the medium.
- B. ITwist off the bottom cap from the SpinTrap™ column and loosen the top cap one-quarter of a turn.
- C. IPlace the column in a 2 mL microcentrifuge tube and centrifuge for 30 s at 70 to 100 × g. Discard the collected liquid.
- Remove and discard the top cap.
- Column equilibration
- A. Add 400 µL binding buffer and centrifuge for 30 s at 800 × g. Discard the collected liquid.
- B. Add 400 µL binding buffer a second time and centrifuge for 30 s at 800 × g. Discard the collected liquid.
- Sample application and incubation
- A. Place the column in a new 2 mL tube.
- B. Dilute the 50 µL plasma sample with binding buffer to a final volume of 100 µL and apply to the column.
- C. Incubate for 5 min without mixing.
- Collection of depleted sample
- A. Centrifuge for 30 s at 800 × g. Collect the eluate.
- B. Add 100 µL binding buffer and centrifuge for 30 s at 800 × g. Collect the eluate.
- C. Add 100 µL binding buffer a second time and centrifuge for 30 s at 800 × g. Collect the eluate.
- Optional: elution of albumin and IgG
- A. Bound albumin and IgG can be eluted by 100 mM glycine-HCl, pH 2.7.
Storage
Store at 4 °C to 8 °C in 20% ethanol.
続きを確認するには、ログインするか、新規登録が必要です。
アカウントをお持ちではありませんか?