おすすめの製品
由来生物
mouse
結合体
FITC conjugate
抗体製品の状態
purified from hybridoma cell culture
抗体製品タイプ
primary antibodies
クローン
NE14, monoclonal
フォーム
buffered aqueous solution
分子量
200 kDa
交差性
pig, feline, chicken, bovine, human, mouse, guinea pig, rat
包装
antibody small pack of 25 μL
濃度
~1 mg/mL
詳細
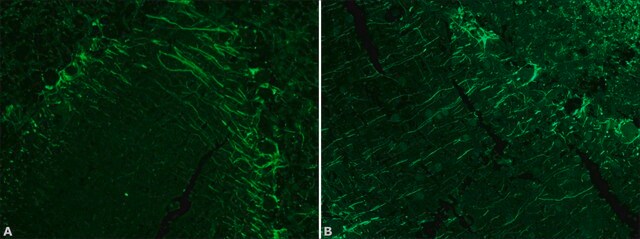
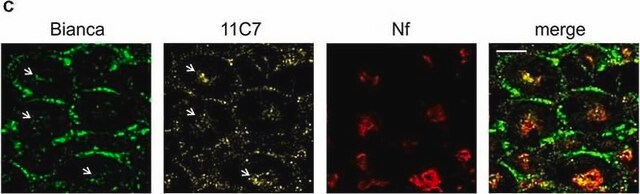
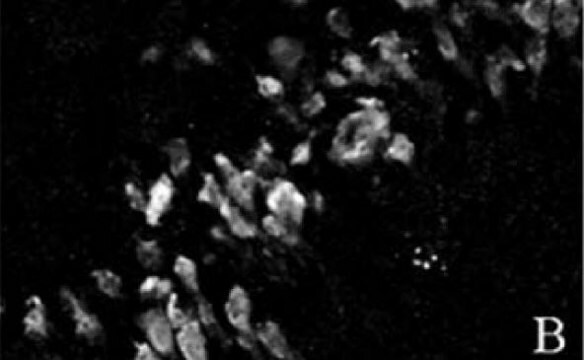
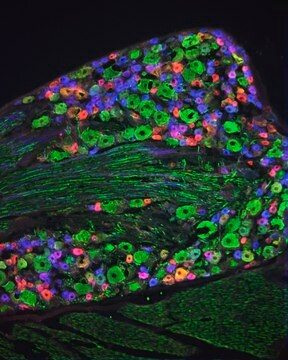
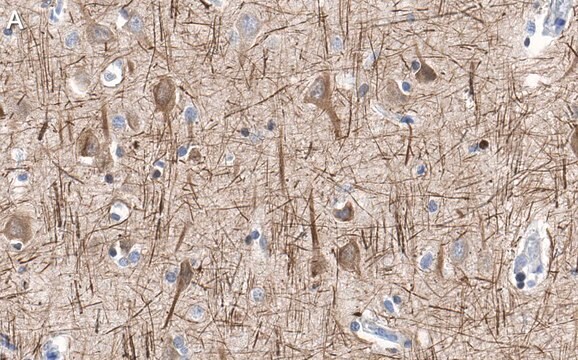
Neurofilaments are type of intermediate filaments (IFs) that serve as major elements of the cytoskeleton supporting the axon cytoplasm of neuronal cells. IFs are components of most eukaryotic cells and significantly differ from other cytoskeletal elements of the cell, namely microtubules and microfilaments.
特異性
Monoclonal Anti-Neurofilament 200, also known as Neurofilament-H or Heavy subunit, specifically recognizes the phosphorylated H tail of Neurofilament 200 and shows no reactivity on enzymatically dephosphorylated neurofilaments.2 The antibody shows reactivity with neurofilaments in the central and peripheral nervous systems from human1, pig1, mouse3, rat4, chicken3, guinea pig3, feline3 and bovine3 origin.
免疫原
Neurofilaments purified from pig spinal cord
アプリケーション
The antibody may be used in various immunochemical techniques including Immunohistochemistry and Immunoblotting (~200 kDa).1-7
生物化学的/生理学的作用
Neurofilaments undergo post-translational modifications including different levels of phosphorylation, which has been suggested to modulate their function by influencing the interaction between neurofilament and cytoplasmic organelles. Neurofilaments are built from three intertwined protofibrils of apparent molecular weights [68 (L), 160 (M) and 200 (H) kDa] which are themselves composed of two tetrameric protofilament complexes of monomeric proteins. Neurofilament 200 also known as Neurofilament heavy polypeptide (H-subunit), NF-H, NEFH or 200 kDa neurofilament protein, has an important function in mature axons that is not subserved by the two smaller neurofilament proteins.
物理的形状
Supplied as a solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide as a preservative.
保管および安定性
For continuous use, store at 2-8°C for up to one month. For extended storage, freeze in working aliquots. Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. If slight turbidity occurs upon prolonged storage, clarify the solution by centrifugation before use. Working dilution samples should be discarded if not used within 12 hours. Protect from prolonged exposure to light.
免責事項
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
適切な製品が見つかりませんか。
製品選択ツール.をお試しください
保管分類コード
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
nwg
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
IRO97106:
SAB4200811-BULK:
SAB4200811-25UL:
SAB4200811-100UL:
SAB4200811-VAR:
最新バージョンのいずれかを選択してください:
D Dahl
Journal of neuroscience research, 20(4), 431-441 (1988-08-01)
Neurofilament phosphorylation in rat nervous system development was studied by indirect immunofluorescence with monoclonal antibodies reacting with phosphorylated epitopes in tissue sections and in primary dissociated cultures. The antibodies either decorated neurofilaments shortly after their appearance or after a considerable
E Debus et al.
Differentiation; research in biological diversity, 25(2), 193-203 (1983-01-01)
A panel of 10 mouse monoclonal antibodies specific for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFA) has been isolated using porcine GFA as antigen. Although all antibodies recognize GFA purified from porcine spinal cord in the western blot technique, they can be
G Shaw et al.
European journal of cell biology, 42(1), 1-9 (1986-10-01)
The work of the Sternbergers and their colleagues has shown that monoclonal antibodies reactive with neurofilament subunit proteins may be sensitive to the state of phosphorylation of these proteins. We therefore examined the ability of our previously described panel of
Y-L Liu et al.
Spinal cord, 47(2), 166-170 (2008-07-30)
Observational cross-section study. The objective of our study was to determine if phosphorylation of aggregated neurofilaments (NFs) would occur in autoimmune-mediated motor neuron injury. Our main hypothesis was that autoimmune-mediated damage of spinal cord motor neurons may influence NF phosphorylation
Ben G Szaro et al.
Trends in neurosciences, 33(1), 27-37 (2009-11-13)
Neurofilament (NF) protein expression is coupled to axon development and the maintenance of neuronal homeostasis. Here, we present evidence that this tight regulation depends critically on post-transcriptionally regulated changes in NF mRNA transport, translation and stability. Recent studies have shown
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)