X0626
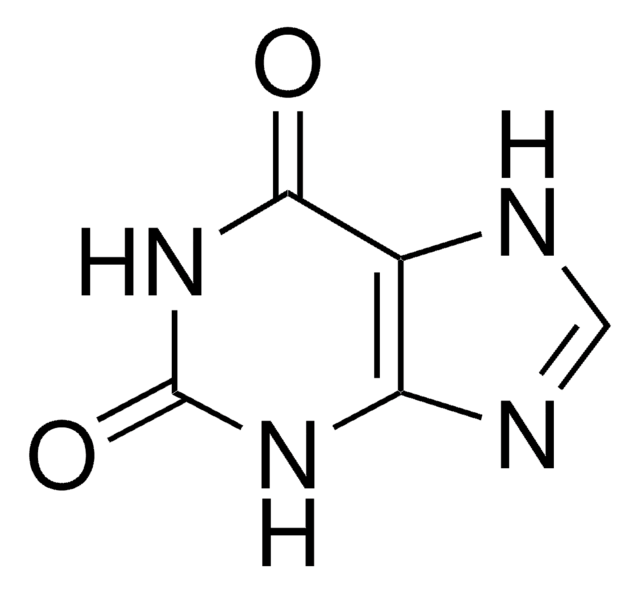
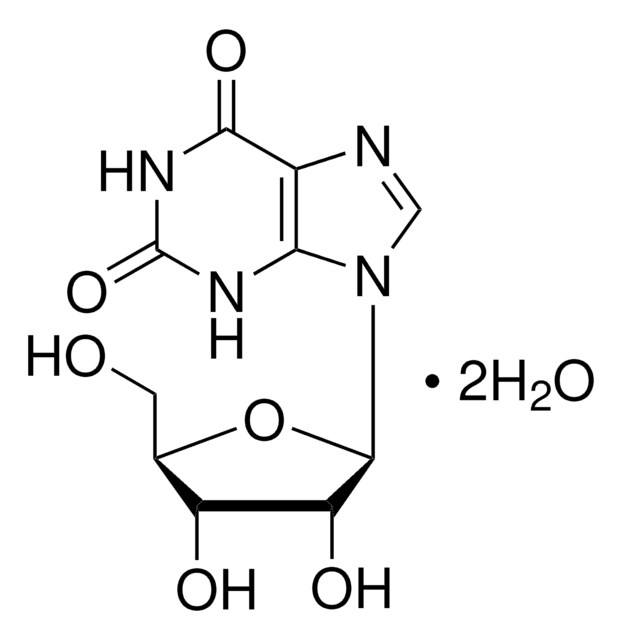
Xanthine
≥99.5% (HPLC), purified by recrystallization
Synonym(s):
2,6-Dioxopurine, 3,7-Dihydropurine-2,6-dione, Xanthin, 2,6-Dihydroxypurine
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥99.5% (HPLC)
form
powder
purified by
recrystallization
solubility
1 M NaOH: soluble 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless to faintly yellow
SMILES string
O=C1NC(=O)c2nc[nH]c2N1
InChI
1S/C5H4N4O2/c10-4-2-3(7-1-6-2)8-5(11)9-4/h1H,(H3,6,7,8,9,10,11)
InChI key
LRFVTYWOQMYALW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Biochem/physiol Actions
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Personal Protective Equipment
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
X0626-100G:
X0626-1G:
X0626-25G:
X0626-5G:
X0626-BULK:
X0626-VAR:
X0626-10G:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Xanthine is a purine base found in most human body tissues and fluids as well as in other organisms. Methylated xanthines (methylxanthines), which include caffeine, paraxanthine, theobromine, and theophylline, commonly used for their effects as mild stiµlants and as bronchodilators, notably in the treatment of asthma symptoms. This application shows the efficient separation of several common xanthines and may be applied their analysis in any number of desired matrices.
Protocols
Enzymatic Assay of Superoxide Dismutase
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service