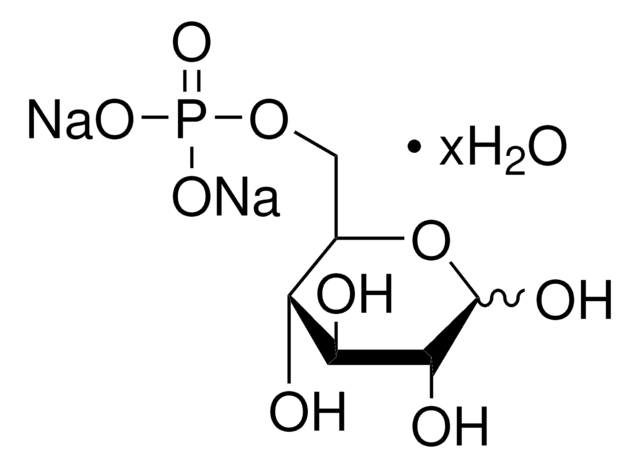
MAK014
Glucose-6-Phosphate Assay Kit
sufficient for 100 colorimetric tests
About This Item
Recommended Products
usage
sufficient for 100 colorimetric tests
detection method
colorimetric
relevant disease(s)
hematological disorder
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Application
- glucose 6-phosphate (G6P) assay
- quantification of glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) and fructose-6-phosphate (F6P)
- metabolite analysis
Suitability
Principle
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class Code
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
PDSCL
Please refer to KIT Component information
PRTR
Please refer to KIT Component information
FSL
Please refer to KIT Component information
ISHL Indicated Name
Please refer to KIT Component information
ISHL Notified Names
Please refer to KIT Component information
Cartagena Act
Please refer to KIT Component information
JAN Code
キットコンポーネントの情報を参照してください
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
We presents an article about the Warburg effect, and how it is the enhanced conversion of glucose to lactate observed in tumor cells, even in the presence of normal levels of oxygen. Otto Heinrich Warburg demonstrated in 1924 that cancer cells show an increased dependence on glycolysis to meet their energy needs, regardless of whether they were well-oxygenated or not.
Protocols
Enzymatic Method for Determining Glucose-6-Phosphate (Glucose-6-Phosphate Assay)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service