11039
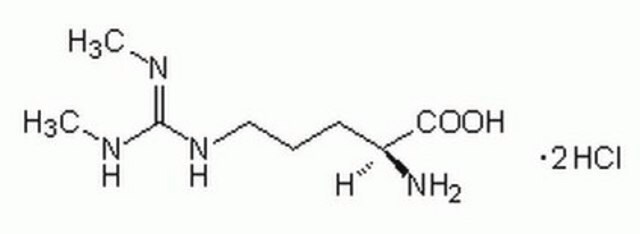
L-Arginine monohydrochloride
≥99.5% (AT), suitable for ligand binding assays, BioUltra
Synonym(s):
(S)-(+)-2-Amino-5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]pentanoic acid monohydrochloride, (S)-(+)-Arginine hydrochloride
About This Item
Recommended Products
product name
L-Arginine monohydrochloride, BioUltra, ≥99.5% (AT)
product line
BioUltra
Quality Level
Assay
≥99.5% (AT)
form
powder or crystals
optical activity
[α]20/D +22.0±0.5°, c = 5% in 5 M HCl
technique(s)
ligand binding assay: suitable
impurities
insoluble matter, passes filter test
≤0.3% foreign amino acids
ign. residue
≤0.05%
loss
≤0.05% loss on drying, 20 °C (HV)
color
colorless
pH
5.5-7.0 (25 °C, 1 M in H2O)
mp
220-230 °C
solubility
H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless
density
1.42 g/cm3 at 20 °C
anion traces
sulfate (SO42-): ≤50 mg/kg
cation traces
Al: ≤5 mg/kg
As: ≤0.1 mg/kg
Ba: ≤5 mg/kg
Bi: ≤5 mg/kg
Ca: ≤10 mg/kg
Cd: ≤5 mg/kg
Co: ≤5 mg/kg
Cr: ≤5 mg/kg
Cu: ≤5 mg/kg
Fe: ≤5 mg/kg
K: ≤50 mg/kg
Li: ≤5 mg/kg
Mg: ≤5 mg/kg
Mn: ≤5 mg/kg
Mo: ≤5 mg/kg
Na: ≤50 mg/kg
Ni: ≤5 mg/kg
Pb: ≤5 mg/kg
Sr: ≤5 mg/kg
Zn: ≤5 mg/kg
λ
1 M in H2O
UV absorption
λ: 260 nm Amax: ≤0.2
λ: 280 nm Amax: ≤0.1
SMILES string
Cl[H].N[C@@H](CCCNC(N)=N)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C6H14N4O2.ClH/c7-4(5(11)12)2-1-3-10-6(8)9;/h4H,1-3,7H2,(H,11,12)(H4,8,9,10);1H/t4-;/m0./s1
InChI key
KWTQSFXGGICVPE-WCCKRBBISA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Storage Class Code
13 - Non Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
11039-500G:
11039-25G:
11039-100G:
11039-BULK:
11039-VAR:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic relaxation of the mouse
anococcygeus muscle
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service