A1330000
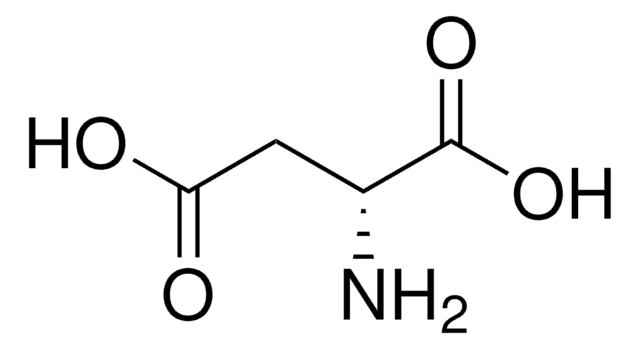
Aspartic acid
European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard
Synonym(s):
L-Aspartic acid, (S)-(+)-Aminosuccinic acid, (S)-Aminobutanedioic acid
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
pharmaceutical primary standard
API family
aspartic acid
manufacturer/tradename
EDQM
mp
>300 °C (dec.) (lit.)
application(s)
pharmaceutical (small molecule)
format
neat
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H7NO4/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h2H,1,5H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)/t2-/m0/s1
InChI key
CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Packaging
Other Notes
related product
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
A1330000-50MG:
A1330000:
A1330000-1EA:
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Protocols
Separation of L-Alanine; Glycine; L-Valine; L-Leucine; L-Isoleucine; L-Proline; L-Methionine; L-Serine; L-Threonine; L-Phenylalanine; L-Aspartic acid; L-4-Hydroxyproline; L-Cysteine; L-Glutamic acid; L-Asparagine; L-Lysine; L-Glutamine; L-Histidine; L-Tyrosine; L-Tryptophan; L-Cystine
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service