764760
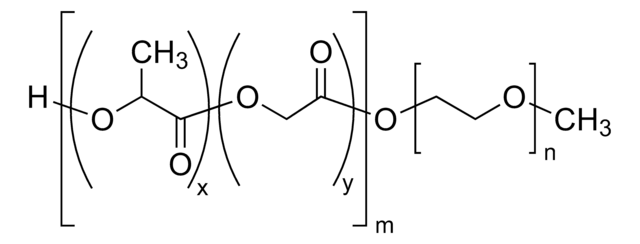
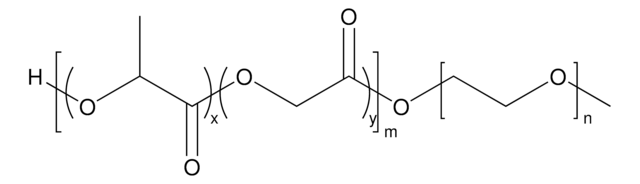
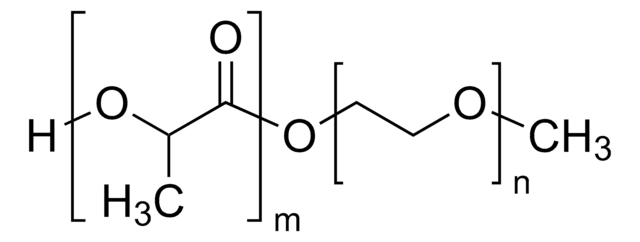
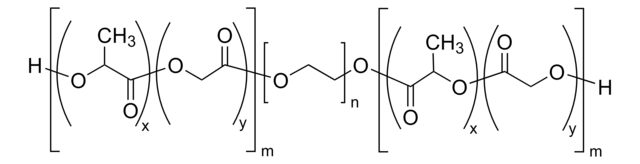
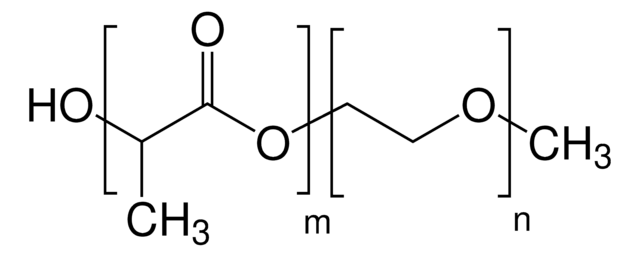
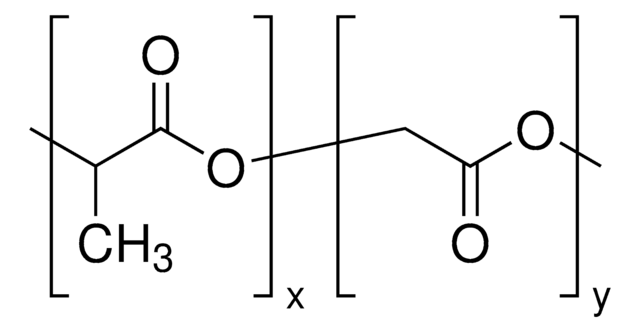
Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether-block-poly(lactide-co-glycolide)
PEG average Mn 2,000, PLGA average Mn 11,500
Synonym(s):
PEG-PLGA, Polyethylene glycol, mPEG-b-PLGA
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
pellets
feed ratio
lactide:glycolide 50:50
mol wt
PEG average Mn 2,000
PLGA average Mn 11,500
average Mn 13,500 (total)
degradation timeframe
1-4 weeks
transition temp
Tm 298-303 °C
Tg 40 °C (PDLLA block)
Tg 6 °C (PEG block)
PDI
≤2.0
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Features and Benefits
- Good biocompatibility, low immunogenicity and good degradability.
- Properties can be easily modulated by changing the block copolymer segment sizes to suit a particular application.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
764760-VAR:
764760-1G:
764760-BULK:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
One of the common difficulties with intravenous drug delivery is low solubility of the drug. The requirement for large quantities of saline to dissolve such materials limits their clinical use, and one solution for this problem that has recently generated interest is the formation of drug-loaded micelles.
Local delivery of bioactive molecules using an implantable device can decrease the amount of drug dose required as well as non-target site toxicities compared to oral or systemic drug administration.
Microparticle drug delivery systems have been extensively researched and applied to a wide variety of pharmaceutical and medical applications due to a number of advantages including injectability, local applicability to target tissues and sites, and controlled drug delivery over a given time period.
Aliphatic polyesters such as polylactide, poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and polycaprolactone, as well as their copolymers, represent a diverse family of synthetic biodegradable polymers that have been widely explored for medical uses and are commercially available.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service