735094
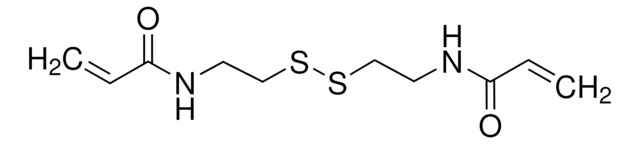
Bis(2-methacryloyl)oxyethyl disulfide
contains ≤6000 ppm hydroquinone as stabilizer
Synonym(s):
DSDMA, Disulfide-based dimethacrylate
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
liquid
Quality Level
contains
≤6000 ppm hydroquinone as stabilizer
refractive index
n20/D 1.517
density
1.141 g/mL at 25 °C
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
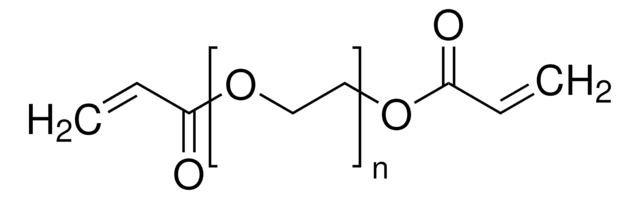
CC(=C)C(=O)OCCSSCCOC(=O)C(C)=C
InChI
1S/C12H18O4S2/c1-9(2)11(13)15-5-7-17-18-8-6-16-12(14)10(3)4/h1,3,5-8H2,2,4H3
InChI key
CGDNFXSLPGLMHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
General description
Application
- Used as a crosslinker in the synthesis of reduction-responsive molecularly imprinted polymer (MIPs) nanogels for drug delivery applications. This reduction-responsive property allows for control over drug delivery and modulation of the release properties of the MIPs.
- Used as a crosslinker in the synthesis of self-healing polymer nanocomposites via dynamic disulfide exchange reaction and crosslinking properties. These self-healing polymer nanocomposites can be used in coatings, electronics, and packaging applications.
- Used as a redox-responsive cross-linker in the synthesis of zwitterionic hydrogels for effective drug delivery. DSDMA provides structural stability, redox-responsiveness, and self-healing properties, which are essential for effective drug delivery.
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 2
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
ISHL Indicated Name
Substances Subject to be Indicated Names
ISHL Notified Names
Substances Subject to be Notified Names
JAN Code
735094-BULK:
735094-5G:4548173925998
735094-VAR:
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service