221015
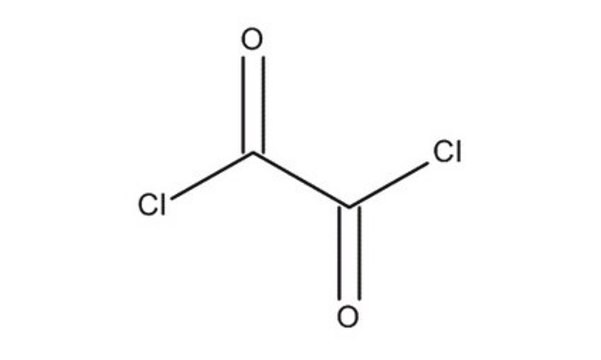
Oxalyl chloride
ReagentPlus®, ≥99%
Synonym(s):
Ethanedioyl dichloride
About This Item
Recommended Products
vapor density
4.4 (vs air)
Quality Level
vapor pressure
150 mmHg ( 20 °C)
product line
ReagentPlus®
Assay
≥99%
form
liquid
reaction suitability
reagent type: oxidant
impurities
<10 ppb Heavy metals
color
APHA: 0-150
refractive index
n20/D 1.429 (lit.)
bp
62-65 °C (lit.)
mp
−10-−8 °C (lit.)
density
1.5 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.)
functional group
acyl chloride
SMILES string
ClC(=O)C(Cl)=O
InChI
1S/C2Cl2O2/c3-1(5)2(4)6
InChI key
CTSLXHKWHWQRSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
- Preparation of Mosher′s acid chloride by reacting with Mosher′s acid in the presence of DMF.
- Activation of dimethyl sulfoxide for use in the oxidation of long-chain alcohols to carbonyls.
- Activation of α-keto carboxylic acids and N-heterocyclic carboxylic acids for alkynylation to form ynediones and N-heterocyclic ynones, respectively.
- Synthesis of N-heterocyclic ynones and ynediones, used to activate carboxylic acids
- Chlorination and halogenation
- Three-component [3+2] cycloadditions
- Reactions with organostannanes
- Synthesis of cyclopentenones
- Carbonylations, used as a carbonyl synthon
Packaging
Legal Information
accessory
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Skin Corr. 1B - Water-react 1
Supplementary Hazards
Storage Class Code
4.3 - Hazardous materials which set free flammable gases upon contact with water
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
51.8 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
11.0 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
221015-10KG:
221015-VAR:
221015-5G:
221015-25G:
221015-BULK:
221015-100G:
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service