SML1817
BCI-121
≥98% (HPLC)
Sinonimo/i:
4-(Aminocarbonyl)-N-(4-bromophenyl)-1-piperidineacetamide, BCI121
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥98% (HPLC)
Stato
powder
Colore
white to beige
Solubilità
DMSO: 20 mg/mL, clear
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Stringa SMILE
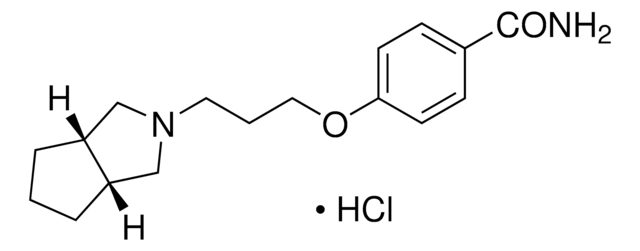
Brc1ccc(cc1)NC(=O)CN2CCC(CC2)C(=O)N
InChI
1S/C14H18BrN3O2/c15-11-1-3-12(4-2-11)17-13(19)9-18-7-5-10(6-8-18)14(16)20/h1-4,10H,5-9H2,(H2,16,20)(H,17,19)
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Non trovi la versione di tuo interesse?
Se hai bisogno di una versione specifica, puoi cercare il certificato tramite il numero di lotto.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.