M5028
Monoclonal Anti-5MTH Folic Acid antibody produced in mouse
clone FA-24, ascites fluid
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
mouse
Livello qualitativo
Coniugato
unconjugated
Forma dell’anticorpo
ascites fluid
Tipo di anticorpo
primary antibodies
Clone
FA-24, monoclonal
contiene
15 mM sodium azide
tecniche
indirect ELISA: 1:5,000
Isotipo
IgG2b
Condizioni di spedizione
dry ice
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
modifica post-traduzionali bersaglio
unmodified
Descrizione generale
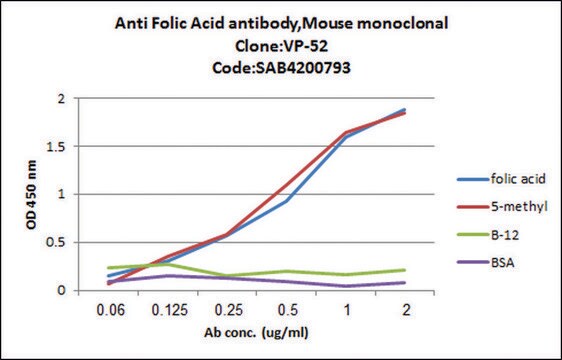
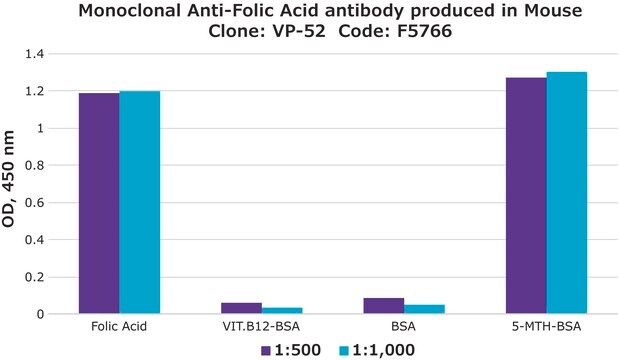
Monoclonal Anti-5MTH Folic Acid antibody is specific for an epitope present on 5MTHFA and does not detect folic acid. This hybridoma is a cloned cell line derived from a fusion between a mouse myeloma cell line and splenocytes from BALB/c mice immunized with 5MTH Folic acid conjugated to KLH.
Immunogeno
5MTH folic acid, conjugated to KLH.
Applicazioni
Monoclonal Anti-5MTH Folic Acid antibody is suitable for use in indirect (Enzyme Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay) ELISA (1:5,000) and competitive ELISA.
Monoclonal Anti-5MTH Folic Acid antibody is suitable for use in indirect ELISA (1:5,000).
Azioni biochim/fisiol
5-Methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF) is a cofactor that regulates the conversion of homocysteine to methionine in the presence of another co-factor, vitamin B12. 5-MTHF is also involved in modulating antioxidative and cognitive functions. Increased serum 5-MTHF levels have been linked to anemia and macrocytosis. The antibody reacts with 5MTHFA as a free reagent or when conjugated to carriers such as KLH or BSA. Furthermore, the product associates with 5MTHFA bound to the endogenous folate binder in human plasma and serum. The monoclonal antibody does not cross-react with tetrahydrofolic acid, folinic acid, dihydrofolic acid, and vitamin B12.
Vitamin B12 and folic acid are metabolically interrelated. The enzyme methionine synthetase, which catalyzes the conversion of homocysteine to methionine, requires vitamin B12 and 5MTHFA as cofactors. In the absence of vitamin B12, 5MTHFA cannot be converted to tetra hydro folic acid and enter the metabolic pool of 1-carbon fragment acceptors. Vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies are the most common causes of megaloblastic anemia, abnormal hemopoiesis, interference in the maintenance of normal nerve tissue and general intracellular uptake and function disorders in humans. Folic acid deficiency is common in pregnant women, alcoholics, those whose diets do not include raw fruits and vegetables and people with structural or functional damage to the small intestine.
Esclusione di responsabilità
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Non trovi il prodotto giusto?
Prova il nostro Motore di ricerca dei prodotti.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
nwg
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Non trovi la versione di tuo interesse?
Se hai bisogno di una versione specifica, puoi cercare il certificato tramite il numero di lotto.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Bashir M Rezk et al.
FEBS letters, 555(3), 601-605 (2003-12-17)
The presumed protective effect of folic acid on the pathogenesis of cardiovascular, hematological and neurological diseases and cancer has been associated with the antioxidant activity of folic acid. Peroxynitrite (PON) scavenging activity and inhibition of lipid peroxidation (LPO) of the
Martha Savaria Morris et al.
The American journal of clinical nutrition, 91(6), 1733-1744 (2010-04-02)
Folate deficiency has serious consequences for the fetus. Folic acid fortification of food addresses this problem. However, clinical consequences of vitamin B-12 deficiency may be worsened by high folic acid intakes, perhaps as a direct result of unmetabolized folic acid
Folic acid deficiency and cancer: mechanisms of DNA instability
Duthie S J.
British Medical Bulletin, 55(3), 578-592 (1999)
Intestinal absorption of folic acid - new physiologic & molecular aspects
Milman, N.
The Indian Journal of Medical Research, 136(5), 725-725 (2012)
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.