L2515
Lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus
bacterial cell wall polymer
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
Staphylococcus aureus
Livello qualitativo
Stato
lyophilized powder
Gruppo funzionale
phospholipid
Tipo di lipide
polymerizable lipids
Condizioni di spedizione
ambient
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Categorie correlate
Descrizione generale
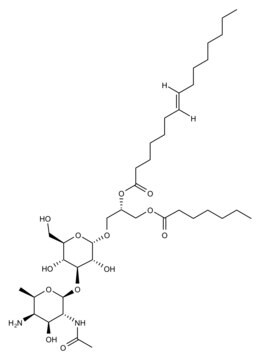
Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) is a linear polymer of phosphodiester-linked glycerol phosphate covalently bound to a lipid. The C2 position on the glycerol-phosphate is usually glycosylated or D-alanylated. LTA is amphipathic due to the presence of the negatively charged backbone of glycerol phosphate and the hydrophobic lipid. The lipid portion is bound hydrophobically to the cell membrane, whereas the polyglycerol phosphate portion extends into the cell wall.
Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) is a teichoic acid attached to a lipid abundant on Gram-positive bacteria cell wall. LTA is a pathogen-associated molecular-patterns (PAMP) recognized by Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), This recognition leads to the activation of NF-kB.
Applicazioni
Lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus has been used:
- to investigate the binding properties of SpHyastatin to lipopolysaccharides and lipoteichoic acid using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- to measure the interleukin (IL-6) produced in splenocytes using a sandwich ELISA
- as a toll-like receptor 2/6 (TLR2/6) agonist to explore its potential to induce tumoricidal M1 macrophage phenotype
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) is a complex component of cell walls of Gram-positive bacteria that are involved in a wide range of cell processes such as the stimulation of immune responses and cell signaling pathways. LTA differs between species of gram-positive bacteria. Lipoteichoic acid from Streptococcus aureus may be used to compare its structure, immunogenicity and functions versus other bacterial LTAs.
Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) is a complex component of the cell walls of Gram-positive bacteria that are implicated in a wide range of cellular processes such as the stimulation of immune responses and cell signaling pathways. LTA differs between species of Gram-positive bacteria. Lipoteichoic acid from Streptococcus aureus may be used to compare its structure, immunogenicity, and functions versus other bacterial LTAs.
Prodotti correlati
N° Catalogo
Descrizione
Determinazione del prezzo
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Simin Rezania et al.
Cancer cell international, 14, 54-54 (2014-06-27)
Many types of tumors are organized in a hierarchy of heterogeneous cell populations with different molecular signature. Such heterogeneity may be associated with different responsiveness to microenvironment stimuli. In the present study, the effects of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and lipoteichoic acid
S Morath et al.
The Journal of experimental medicine, 193(3), 393-397 (2001-02-07)
Lipoteichoic acids (LTAs) have been proposed as putative Gram-positive immunostimulatory counterparts to Gram-negative lipopolysaccharides. However, LTA from Staphylococcus aureus, the clinically most frequent Gram-positive pathogen, was inactive after purification. Here, a novel isolation procedure to prepare pure (>99%) biologically active
Varenka J Barbero-Becerra et al.
World journal of gastroenterology, 17(10), 1317-1325 (2011-04-02)
To study the role of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria in the pathogenesis of liver injury, specifically the activation of inflammatory mediators. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells of 20 out-patients were studied, 10 of them with cirrhosis. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were
Nien-Tzu Chou et al.
Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2012, 735396-735396 (2013-01-11)
Chlorella sorokiniana (CS) is a unicellular green alga. The extracts of Chlorella have been used as treatments for relieving hypertension and modulating immune response. The detailed mechanisms are not clear yet. In this study, we sought to study the molecular
Gopinath Kasetty et al.
Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 55(6), 2880-2890 (2011-03-16)
Peptides of the C-terminal region of human thrombin are released upon proteolysis and identified in human wounds. In this study, we wanted to investigate minimal determinants, as well as structural features, governing the antimicrobial and immunomodulating activity of this peptide
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.