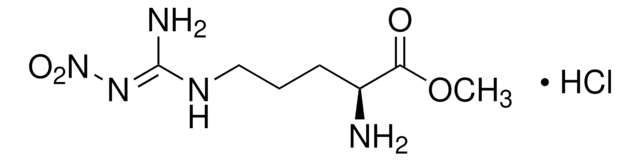
K0250
Kainic acid monohydrate
≥99% (TLC), powder, ionotropic glutamate receptor (kainate class) agonist
Sinonimo/i:
Digenin, Kainate, 2-Carboxy-3-carboxymethyl-4-isopropenylpyrrolidine
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
product name
Kainic acid monohydrate, ≥99% (TLC)
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥99% (TLC)
Forma fisica
powder
Impurezze
Glutamate, free
Solubilità
H2O: soluble
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Stringa SMILE
O.CC(=C)[C@H]1CN[C@@H]([C@H]1CC(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C10H15NO4.H2O/c1-5(2)7-4-11-9(10(14)15)6(7)3-8(12)13;/h6-7,9,11H,1,3-4H2,2H3,(H,12,13)(H,14,15);1H2/t6-,7+,9-;/m0./s1
FZNZRJRSYLQHLT-SLGZUKMRSA-N
Informazioni sul gene
human ... GRIA1(2890) , GRIA2(2891) , GRIA4(2893) , GRIK1(2897) , GRIK2(2898) , GRIK3(2899) , GRIK4(2900) , GRIK5(2901) , SLC1A1(6505) , SLC1A2(6506) , SLC1A3(6507)
mouse ... Gria1(14799)
rat ... Gria1(50592) , Grik1(29559) , Grik4(24406) , Grin2a(24409)
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
- tostudy mechanisms of excitation-induced apoptosis and epilepsy.
- to hamper themitochondrial function ()
- used to induce c-fosexpression in the mice′s brains, specifically targeting the dorsal hippocampus.()
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
Nota sulla preparazione
Prodotti correlati
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.