F3685
Fibroblast Growth Factor-Basic
FGF-Basic, from human, recombinant, expressed in E. coli, carrier free
Sinonimo/i:
FGB-b, FGF-2, HBGF-2, HBGH-2, Prostatropin, bFGF
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
human
Livello qualitativo
Ricombinante
expressed in E. coli
Saggio
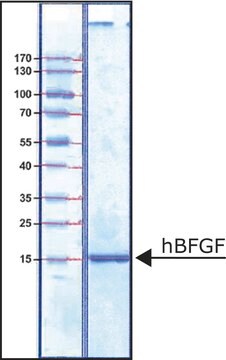
≥97% (SDS-PAGE)
Forma fisica
lyophilized powder
Potenza
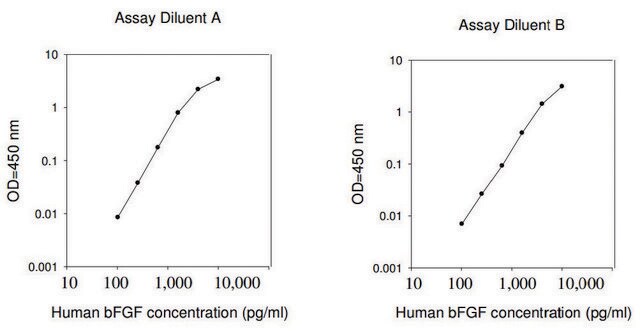
<1 ng/mL Biological Activity EC50
PM
16.0 kDa
Confezionamento
pkg of 4X25 μg
pkg of 25 μg
Condizioni di stoccaggio
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
Colore
white to faint yellow cast
Solubilità
water: soluble 0.025 mg, clear, colorless to faintly yellow
N° accesso UniProt
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Informazioni sul gene
human ... FGF2(2247)
Descrizione generale
Citazione
2. Gospodarowicz, D. et al., Structural characterization and biological functions of fibroblast growth factor. Endo. Rev., 8, 95-114 (1987).
3. Esch, F. et al., Primary structure of bovine pituitary basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and comparison with the amino-terminal sequence of bovine brain acidic FGF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 82, 6507-6511 (1985).
4. Neufeld, G., and Gospodarowicz, D., Basic and acidic fibroblast growth factors interact with the same cell surface receptors. J. Biol. Chem., 261, 5631-5637 (1986).
5. Lobb, R.R. et al., Purification of heparin-binding growth factors. Anal. Biochem., 154, 1-14 (1986).
6. Abraham, J.A., Human basic fibroblast growth factor: nucleotide sequence and genomic organization. EMBO J., 5, 2523- 2528 (1986).
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.