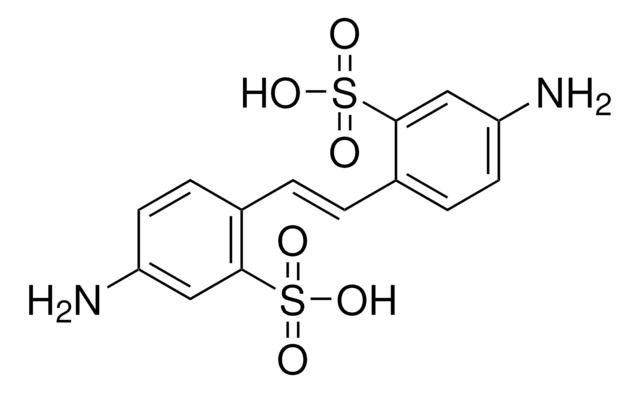
D3514
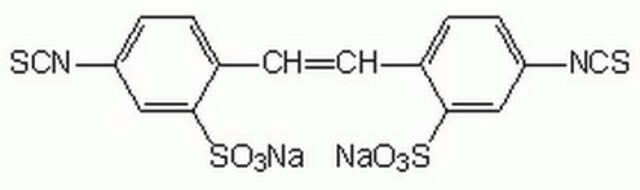
4,4′-Diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid disodium salt hydrate
≥80% (elemental analysis), powder
Sinonimo/i:
DIDS, Disodium 4,4′-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2′-disulfonate
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Grado
for analytical purposes
Saggio
≥80% (elemental analysis)
Stato
powder
Impiego in reazioni chimiche
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
Colore
yellow
Solubilità
0.1 M potassium bicarbonate: 50 mg/mL
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Stringa SMILE
[Na+].[Na+].[O-]S(=O)(=O)c1cc(ccc1\C=C\c2ccc(cc2S([O-])(=O)=O)N=C=S)N=C=S
InChI
1S/C16H10N2O6S4.2Na/c19-27(20,21)15-7-13(17-9-25)5-3-11(15)1-2-12-4-6-14(18-10-26)8-16(12)28(22,23)24;;/h1-8H,(H,19,20,21)(H,22,23,24);;/q;2*+1/p-2/b2-1+;;
GEPAYBXVXXBSKP-SEPHDYHBSA-L
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Applicazioni
- as band3 protein inhibitor in rabbits(19)
- for the inhibition of bicarbonate transporters in brain slice tissue(20)
- as HCO3-/Cl- exchanger (anion exchanger) in embryos(21)
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Eye Irrit. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organi bersaglio
Respiratory system
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.