53747
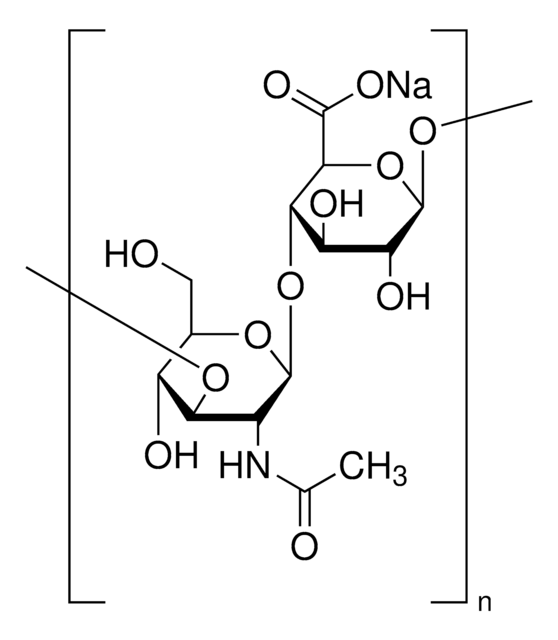
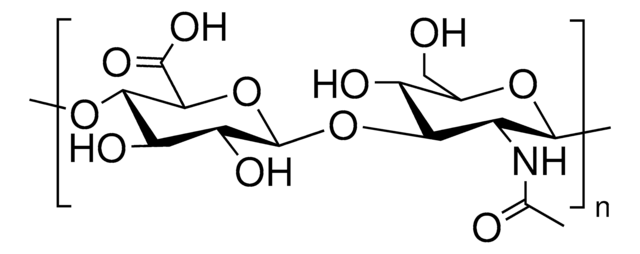
Hyaluronic acid sodium salt from Streptococcus equi
bacterial glycosaminoglycan polysaccharide
Sinonimo/i:
Poly(β-glucuronic acid-[1→3]-β-N-acetylglucosamine-[1→4]), alternating
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
(Streptococcus equi)
Stato
powder or crystals
PM
~1.5-1.8 x 10E6 Da
Impurezze
≤1% protein
Colore
white
Solubilità
H2O: 5 mg/mL, clear, colorless
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Stringa SMILE
[Na+].CC(=O)N[C@@H]1C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)O[C@@H]2C([O-])=O
InChI
1S/C28H44N2O23.Na/c1-5(33)29-9-18(11(35)7(3-31)47-25(9)46)49-28-17(41)15(39)20(22(53-28)24(44)45)51-26-10(30-6(2)34)19(12(36)8(4-32)48-26)50-27-16(40)13(37)14(38)21(52-27)23(42)43;/h7-22,25-28,31-32,35-41,46H,3-4H2,1-2H3,(H,29,33)(H,30,34)(H,42,43)(H,44,45);/q;+1/t7-,8-,9-,10-,11-,12-,13+,14+,15-,16-,17-,18-,19-,20+,21+,22+,25-,26+,27-,28-;/m1./s1
YWIVKILSMZOHHF-QJZPQSOGSA-N
Categorie correlate
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
- with methacrylic anhydride for synthesizing cross-linkable methacrylated HA hydrogel (Coll-MeHA)
- in phosphate buffer saline (PBS) to replace the PBS bath to vary the lubricant composition
- in the preparation of lubricant to study its effects on the boundary lubrication of human osteoarthritis (OA) cartilage
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Altre note
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 2
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
Glycosaminoglycans are large linear polysaccharides constructed of repeating disaccharide units.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.