07743
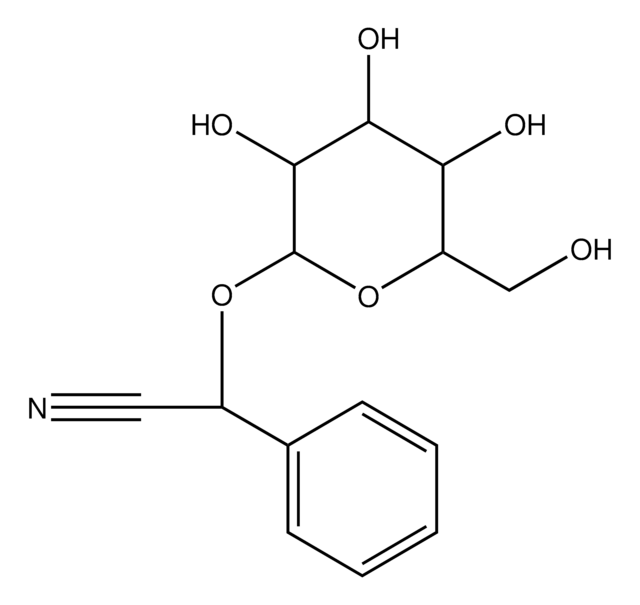
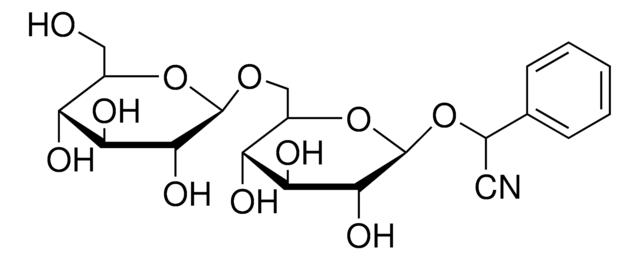
Dhurrin
≥95% (HPLC)
Sinonimo/i:
(S)-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile, (S)-4-Hydroxymandelonitrile β-D-glucoside
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Saggio
≥95% (HPLC)
Forma fisica
powder or crystals
Colore
white to light brown
Temperatura di conservazione
room temp
Stringa SMILE
OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O[C@H](C#N)c2ccc(O)cc2)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O
InChI
1S/C14H17NO7/c15-5-9(7-1-3-8(17)4-2-7)21-14-13(20)12(19)11(18)10(6-16)22-14/h1-4,9-14,16-20H,6H2/t9-,10-,11-,12+,13-,14-/m1/s1
NVLTYOJHPBMILU-YOVYLDAJSA-N
Descrizione generale
Confezionamento
Altre note
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.