36650
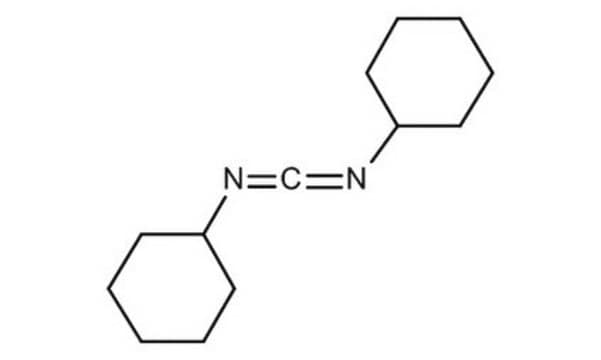
DCC
≥99.0% (GC), for peptide synthesis
Sinonimo/i:
N,N′-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
product name
DCC, puriss., ≥99.0% (GC)
Grado
puriss.
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥99.0% (GC)
Forma fisica
solid
Impiego in reazioni chimiche
reaction type: Coupling Reactions
P. eboll.
122-124 °C/6 mmHg (lit.)
Punto di fusione
32.0-37.0 °C
34-35 °C (lit.)
Solubilità
methylene chloride: 0.1 g/mL, clear, colorless
applicazioni
peptide synthesis
Stringa SMILE
C1CCC(CC1)N=C=NC2CCCCC2
InChI
1S/C13H22N2/c1-3-7-12(8-4-1)14-11-15-13-9-5-2-6-10-13/h12-13H,1-10H2
QOSSAOTZNIDXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Informazioni sul gene
human ... EPHX2(2053)
mouse ... Ephx2(13850)
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
It may be also used to synthesize:
- 1,3-Thiazetedine derivatives via [2+2] cycloaddition with 2-phenylethenyl- and 2-(4-nitrophenyl)ethenyl isothiocyanates.
- 1,3,5-Oxadiazine-4-thiones via [4+2] cycloaddition with benzoyl isothiocyanates.
- Sterically hindered 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives by reacting with (N-isocyanimino)triphenylphosphorane the presence of aromatic (or heteroaromatic) carboxylic acids.
Altre note
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
6.1D - Non-combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic hazardous materials or hazardous materials causing chronic effects
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
235.4 °F - closed cup
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
113 °C - closed cup
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
In principle, the seemingly simple formation of a peptide bond can be accomplished using all the procedures available in organic chemistry for the synthesis of carboxylic acid amides. However, due to the presence of various functional groups in natural and unnatural amino acids and particularly the requirement for full retention of chiral integrity, the coupling of amino acids and peptides under mild conditions can be challenging. A plethora of coupling reagents has been developed superseding each other in efficiency and suitability for specific applications (e.g., solid-phase peptide synthesis or fragment condensation).
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.