SCC412
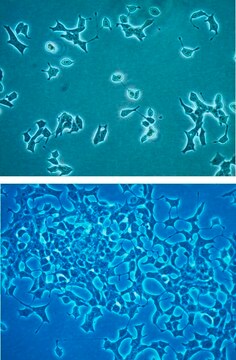
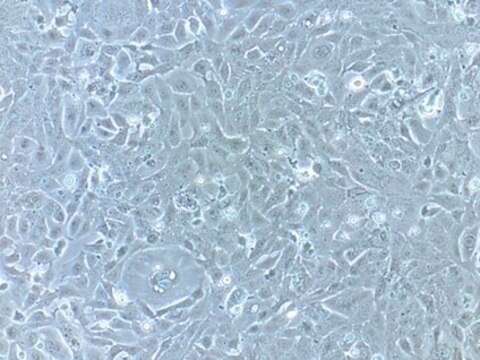
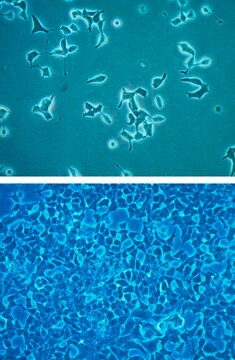
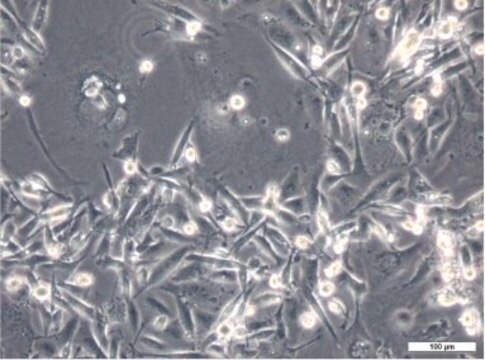
LbetaT2 Mouse Pituitary Gonadotrope Cell Line
Mouse
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Codice UNSPSC:
41106514
NACRES:
NA.45
Prodotti consigliati
Nome del prodotto
LbetaT2 Mouse Pituitary Gonadotrope Cell Line,
Origine biologica
mouse
Confezionamento
vial of >1X10⁶ cells
Produttore/marchio commerciale
Millipore
Modalità di accrescimento
N/A
tecniche
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
Condizioni di spedizione
dry ice
Temperatura di conservazione
≤ − 140°C
Applicazioni
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) plays a key role in the control of reproduction in mammals. GnRH acts via its receptor, GnRH-R, to trigger the synthesis and release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) by the pituitary gonadotropes. In turn, the gonadotropins regulate gametogenesis and steroidogenesis in the gonads. LH and FSH comprise a common glycoprotein hormone subunit, CGA, and the respective specific subunits LH and FSH. The individual subunits bind noncovalently to the common a subunit to form the mature glycoprotein hormones. Lhb gene expression is preferentially induced by high-frequency GnRH pulses, whereas low-frequency pulses favor Fshb expression.
Source.
The immortalized L(betta)T2 mouse pituitary gonadotrope cell line was generated by targeted tumorigenesis in transgenic mice carrying the rat LHb regulatory region linked to the SV40 T-antigen oncogene.1 L(betta)T2 cells express CGA, GnRH-R, and LHb. The cell line responds to pulsatile GnRH stimulation by upregulating Lhb and Gnrhr and secreting LH. The L(betta)T2 cell line has been widely used as an in vitro model for the study of gonadotropin gene regulation and GnRH signaling.2,3,4,5 The global mRNA expression profile and a genome-wide atlas of accessible chromatin in GnRH-stimulated L(betta)T2 cells has recently been described6 and the STR profile has also been reported.7
References
Note: Please include the appropriate references from 1-5 in your publications that utilize them.
1. Alarid ET, Windle JJ, Whyte DB, Mellon PL. Development 1996; 122(10):3319-3329.
2. Turgeon JL, Kimura Y, Waring DW, Mellon PL. Molecular Endocrinology 1996; 10(4):439-450.
3. Thomas P, Mellon PL, Turgeon J, Waring DW. Endocrinology 1996; 137(7):2929-2989.
4. Alarid ET, Holley S, Hayakawa M, Mellon PL. Mol Cell Endocrinol 1998; 140(1-2):25-30.
5. Pernasetti F, Vasilyev VV, Rosenberg SB, Bailey JS, Huang HJ, Miller WL, Mellon PL. Endocrinology 2001; 142(6):2284-2295.
6. Ruf-Zamojski F et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2018; 9:34.
7. Ruf-Zamojski F et al. J Endocr Soc 2019; 3(5):902–920.
Source.
The immortalized L(betta)T2 mouse pituitary gonadotrope cell line was generated by targeted tumorigenesis in transgenic mice carrying the rat LHb regulatory region linked to the SV40 T-antigen oncogene.1 L(betta)T2 cells express CGA, GnRH-R, and LHb. The cell line responds to pulsatile GnRH stimulation by upregulating Lhb and Gnrhr and secreting LH. The L(betta)T2 cell line has been widely used as an in vitro model for the study of gonadotropin gene regulation and GnRH signaling.2,3,4,5 The global mRNA expression profile and a genome-wide atlas of accessible chromatin in GnRH-stimulated L(betta)T2 cells has recently been described6 and the STR profile has also been reported.7
References
Note: Please include the appropriate references from 1-5 in your publications that utilize them.
1. Alarid ET, Windle JJ, Whyte DB, Mellon PL. Development 1996; 122(10):3319-3329.
2. Turgeon JL, Kimura Y, Waring DW, Mellon PL. Molecular Endocrinology 1996; 10(4):439-450.
3. Thomas P, Mellon PL, Turgeon J, Waring DW. Endocrinology 1996; 137(7):2929-2989.
4. Alarid ET, Holley S, Hayakawa M, Mellon PL. Mol Cell Endocrinol 1998; 140(1-2):25-30.
5. Pernasetti F, Vasilyev VV, Rosenberg SB, Bailey JS, Huang HJ, Miller WL, Mellon PL. Endocrinology 2001; 142(6):2284-2295.
6. Ruf-Zamojski F et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2018; 9:34.
7. Ruf-Zamojski F et al. J Endocr Soc 2019; 3(5):902–920.
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
The LbetaT2 cell line has been widely used as an in vitro model for the study of gonadotropin gene regulation and GnRH signaling
Stoccaggio e stabilità
The cells should be stored in liquid nitrogen. The cells can be cultured for at least 10 passages after initial thawing without significantly affecting the cell marker expression and functionality.
Altre note
This product is intended for sale and sold solely to academic institutions for internal academic research use per the terms of the “Academic Use Agreement” as detailed in the product documentation.
Esclusione di responsabilità
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 2
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.