8.55015
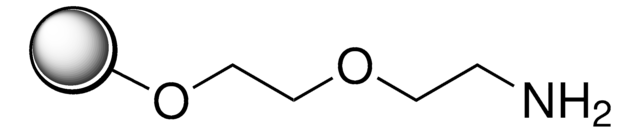
Amino PEGA resin
Novabiochem®
Sinonimo/i:
Amino PEGA resin
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Nome Commerciale
Novabiochem®
PEGA
Stato
beads
Impiego in reazioni chimiche
reaction type: Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis
Produttore/marchio commerciale
Novabiochem®
applicazioni
peptide synthesis
Gruppo funzionale
amine
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Descrizione generale
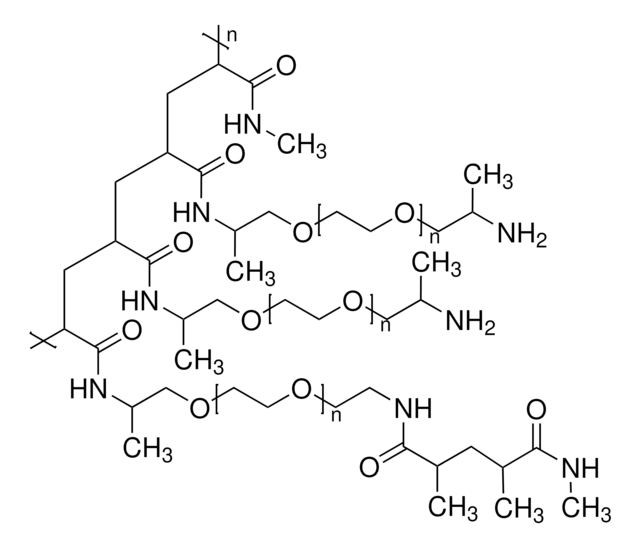
PEGA resins consist of dimethyl acrylamide and mono-2-acrylamidoprop-1-yl[2-aminoprop-1-yl] polyethylene glycol cross-linked with bis 2-acrylamidoprop-1-yl polyethyleneglycol. These supports swell extensively in a wide range of solvents and are permeable to macromolecules up to 35 kD, making them ideal for the preparation of combinatorial libraries, affinity purification and on-resin enzyme assays. For applications of these resins in SPPS and SPOS see [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18].Note: PEGA resins are supplied swollen in ethanol, with 1g dry resin corresponding to approximately 15 mL of swollen resin. As the beads of PEGA resins become very sticky and easily damaged when shrunk or dried, they are best handled in a swollen state. To use, the appropriate amount of swollen resin should be weighed into a reaction vessel and any residual ethanol removed by copious washings with the appropriate solvent or solvent mixture. After peptide assembly, the resin should be washed with DCM and transferred to the cleavage vessel. Excess DCM can be removed under vacuum, and the shrunk resin treated with the TFA cocktail. The characteristics of the swollen resin, its robustness and high permeability enables its use in both batch and continuous flow synthesis apparatus.
Associated Protocols and Technical Articles
Protocols for Loading of Peptide Synthesis Resins Literature references
Literature references
[1] M. Meldal, et al. (1992) Tetrahedron Lett., 33, 3077.
[2] F. I. Auzanneau, et al. (1994) J. Peptide Sci., 1, 31.
[3] M. Meldal in ′Peptides 1992, Proc. 22nd European Peptide Symposium′, C. H. Schneider & A. N. Eberle (Eds), ESCOM, Leiden, 1993, pp.61.
[4] M. Meldal, et al. in ′Innovation & Perspectives in Solid Phase Synthesis, 3rd International Symposium′, R. Epton (Eds), Mayflower Worldwide, Birmingham, 1994, pp. 259.
[5] M. Meldal, et al. (1993) Int. J. Peptide Protein Res., 41, 250.
[6] M. Meldal, et al. (1994) J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 849.
[7] M. Meldal, et al. (1994) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 3314.
[8] M. Renil, et al. (1998) J. Peptide Sci., 4, 195.
[9] J. C. Spetzler, et al. (1998) J. Peptide Sci., 4,128.
[10] M. Meldal, et al. (1998) J. Peptide Sci., 4 ,83.
[11] J. A. Camarero, et al. (1998) J. Peptide Res., 51, 303.
[12] J. A. Camarero, et al. (2000) Lett. Pept. Sci., 7,17.
[13] O. Melnyk, et al. (2001) J. Org. Chem., 66, 4153.
[14] J. Buchardt, et al. (2000) J. Comb. Chem., 2, 624.
[15] J. F. Tolberg, et al. (2002) J. Org. Chem., 67, 4143.
[16] J. Bondebjerg, et al. (2002) J. Am. Chem. Soc., 124, 11046.
[17] J. Tulla-Puche, et al. (2004) J. Org. Chem., 69, 4101.
[18] S. Aggarwal, et al. (2005) Biomaterials, 26, 6077.
Associated Protocols and Technical Articles
Protocols for Loading of Peptide Synthesis Resins Literature references
Literature references
[1] M. Meldal, et al. (1992) Tetrahedron Lett., 33, 3077.
[2] F. I. Auzanneau, et al. (1994) J. Peptide Sci., 1, 31.
[3] M. Meldal in ′Peptides 1992, Proc. 22nd European Peptide Symposium′, C. H. Schneider & A. N. Eberle (Eds), ESCOM, Leiden, 1993, pp.61.
[4] M. Meldal, et al. in ′Innovation & Perspectives in Solid Phase Synthesis, 3rd International Symposium′, R. Epton (Eds), Mayflower Worldwide, Birmingham, 1994, pp. 259.
[5] M. Meldal, et al. (1993) Int. J. Peptide Protein Res., 41, 250.
[6] M. Meldal, et al. (1994) J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 849.
[7] M. Meldal, et al. (1994) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 3314.
[8] M. Renil, et al. (1998) J. Peptide Sci., 4, 195.
[9] J. C. Spetzler, et al. (1998) J. Peptide Sci., 4,128.
[10] M. Meldal, et al. (1998) J. Peptide Sci., 4 ,83.
[11] J. A. Camarero, et al. (1998) J. Peptide Res., 51, 303.
[12] J. A. Camarero, et al. (2000) Lett. Pept. Sci., 7,17.
[13] O. Melnyk, et al. (2001) J. Org. Chem., 66, 4153.
[14] J. Buchardt, et al. (2000) J. Comb. Chem., 2, 624.
[15] J. F. Tolberg, et al. (2002) J. Org. Chem., 67, 4143.
[16] J. Bondebjerg, et al. (2002) J. Am. Chem. Soc., 124, 11046.
[17] J. Tulla-Puche, et al. (2004) J. Org. Chem., 69, 4101.
[18] S. Aggarwal, et al. (2005) Biomaterials, 26, 6077.
Applicazioni
- Fluorescence-Based On-Resin Detection of Three Model Proteases: Discusses the use of Amino PEGA resin modified with backbone amide linker (BAL) for developing solid support-bound probes used in fluorescence-based assays. (Milicevic & Hlavác, 2021).
- Attachment of cyclodextrin acids to PEGA resin and study of binding with fluorescence microscopy: Investigates the attachment of cyclodextrin to amino PEGA resin and evaluates their binding interactions using fluorescence microscopy. (Langhorn et al., 2021).
Linkage
Replaces: 01-64-0100
Risultati analitici
Color (visual): white to yellow to beige
Appearance of substance (visual): beads
Loading (determined from the substitution of the Fmoc-Leu loaded resin): 0.30 - 0.50 mmol/g
Swelling Volume (in DMF): lot specific result
Swelling Volume (in water): lot specific result
dry resin %: lot specific result
The resin is sold swollen in ethanol. 50 - 100 mesh
Appearance of substance (visual): beads
Loading (determined from the substitution of the Fmoc-Leu loaded resin): 0.30 - 0.50 mmol/g
Swelling Volume (in DMF): lot specific result
Swelling Volume (in water): lot specific result
dry resin %: lot specific result
The resin is sold swollen in ethanol. 50 - 100 mesh
Note legali
Novabiochem is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
nwg
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.