05-915
Anti-N-Cadherin Antibody, clone 13A9
culture supernatant, clone 13A9, Upstate®
Sinonimo/i:
Cadherin-2, CD325, CDw325, N-cadherin, Neural cadherin
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
mouse
Livello qualitativo
Forma dell’anticorpo
culture supernatant
Tipo di anticorpo
primary antibodies
Clone
13A9, monoclonal
Reattività contro le specie
human
Confezionamento
antibody small pack of 25 μL
Produttore/marchio commerciale
Upstate®
tecniche
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
western blot: suitable
N° accesso NCBI
N° accesso UniProt
Condizioni di spedizione
ambient
modifica post-traduzionali bersaglio
unmodified
Informazioni sul gene
human ... CDH2(1000)
Categorie correlate
Descrizione generale
Specificità
Immunogeno
Applicazioni
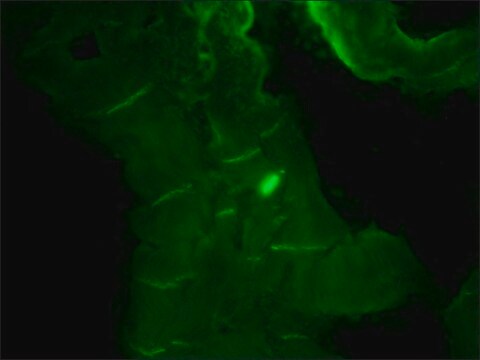
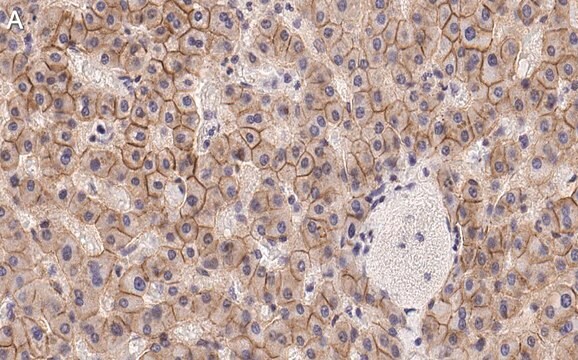
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected strong N-cadherin immunoreactivity in paraffin-embedded rectal cancer (RC) tissues with positive regional lymph node metastasis (RLNM) status, while only weak N-cadherin immunoreactivity was detected in RC with negative RLNM, and no N-cadherin staining was seen in normal colorectal epithelium (Fan, X.J., et al. (2012). Br. J. Cancer. 106(11):1735-1741).
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected N-cadherin immunoreactivity in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissue sections. A significant inverse correlation was found between RUNX3 and N-cadherin expression levels (Tanaka, S., et al. (2012). Int. J. Cancer. 131(11):2537-2546).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected an upregulated N-cadherin expression in CCL185 carcinoma cells following transient Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection. The EMT-like phenotype remained even after viral loss by culture selection pressure withdrawal (Queen, K.J., et al. (2013). Int. J. Cancer. 132(9):2076-2086).
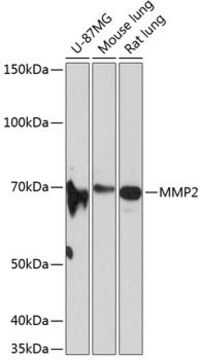
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected N-cadherin in Hep3B, Huh7, HLF and SK-Hep1 human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lysates (Tanaka, S., et al. (2012). Int. J. Cancer. 131(11):2537-2546).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected both the unprocessed (pro-) and processed (mature) forms of N-cadherin in HeLa cell lysate (Wahl, J.K. 3rd., et al. (2003). J. Biol. Chem. 278(19):17269-17276).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected N-cadherin in WI-38 human fibroblast lysate, but not in JAr human placental choriocarcinoma cell lysate (Knudsen, K.A., et al. (1995). J. Cell Biol. 130(1):67-77).
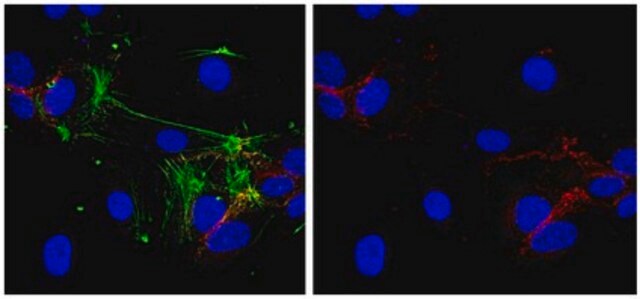
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected N-cadherin immunoreactivity localized primarily at the cell-cell borders by fluorescent immunocytochemistry staining of 1% paraformaldehyde-fixed, methanol-permeabilized HeLa cells (Wahl, J.K. 3rd., et al. (2003). J. Biol. Chem. 278(19):17269-17276).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected N-cadherin immunoreactivity colocalized with those of alpha- and beta-catenin by dual fluorescent immunocytochemistry staining of fixed WI-38 human fibroblasts (Knudsen, K.A., et al. (1995). J. Cell Biol. 130(1):67-77).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: Representative lots co-immunoprecipitated alpha-catenin, beta-catenin, and plakoglobin with N-cadherin from WI-38 human fibroblast and HeLa cell lysates (Wahl, J.K. 3rd., et al. (2003). J. Biol. Chem. 278(19):17269-17276; Knudsen, K.A., et al. (1995). J. Cell Biol. 130(1):67-77).
Cell Structure
Adhesion (CAMs)
Qualità
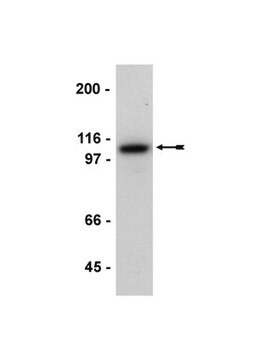
Western Blotting Analysis: A 1:1000-5000 dilution of this hybridoma culture supernatant detected N-cadherin in HeLa cell lysate.
Descrizione del bersaglio
Linkage
Stato fisico
Stoccaggio e stabilità
Risultati analitici
HeLa cell lysate
Note legali
Esclusione di responsabilità
Non trovi il prodotto giusto?
Prova il nostro Motore di ricerca dei prodotti.
Raccomandato
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Articoli
Human iPSC neural differentiation media and protocols used to generate neural stem cells, neurons and glial cell types.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.